Systematic analyses of drugs and disease indications in RepurposeDB reveal pharmacological, biological and epidemiological factors influencing drug repositioning
- PMID: 28200013
- PMCID: PMC6192146
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbw136
Systematic analyses of drugs and disease indications in RepurposeDB reveal pharmacological, biological and epidemiological factors influencing drug repositioning
Abstract
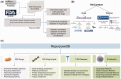
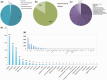
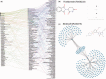
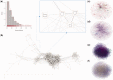
Increase in global population and growing disease burden due to the emergence of infectious diseases (Zika virus), multidrug-resistant pathogens, drug-resistant cancers (cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer) and chronic diseases (arterial hypertension) necessitate effective therapies to improve health outcomes. However, the rapid increase in drug development cost demands innovative and sustainable drug discovery approaches. Drug repositioning, the discovery of new or improved therapies by reevaluation of approved or investigational compounds, solves a significant gap in the public health setting and improves the productivity of drug development. As the number of drug repurposing investigations increases, a new opportunity has emerged to understand factors driving drug repositioning through systematic analyses of drugs, drug targets and associated disease indications. However, such analyses have so far been hampered by the lack of a centralized knowledgebase, benchmarking data sets and reporting standards. To address these knowledge and clinical needs, here, we present RepurposeDB, a collection of repurposed drugs, drug targets and diseases, which was assembled, indexed and annotated from public data. RepurposeDB combines information on 253 drugs [small molecules (74.30%) and protein drugs (25.29%)] and 1125 diseases. Using RepurposeDB data, we identified pharmacological (chemical descriptors, physicochemical features and absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity properties), biological (protein domains, functional process, molecular mechanisms and pathway cross talks) and epidemiological (shared genetic architectures, disease comorbidities and clinical phenotype similarities) factors mediating drug repositioning. Collectively, RepurposeDB is developed as the reference database for drug repositioning investigations. The pharmacological, biological and epidemiological principles of drug repositioning identified from the meta-analyses could augment therapeutic development.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Using a novel computational drug-repositioning approach (DrugPredict) to rapidly identify potent drug candidates for cancer treatment.Oncogene. 2018 Jan 18;37(3):403-414. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.328. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28967908 Free PMC article.
-
Computational drug repositioning through heterogeneous network clustering.BMC Syst Biol. 2013;7 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S6. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-7-S5-S6. Epub 2013 Dec 9. BMC Syst Biol. 2013. PMID: 24564976 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Drug Repositioning with Random Walk on a Heterogeneous Network.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2019 Nov-Dec;16(6):1890-1900. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2018.2832078. Epub 2018 May 2. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 29994051
-
Computational Drug Repositioning: A Lateral Approach to Traditional Drug Discovery?Curr Top Med Chem. 2016;16(19):2069-77. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666160216153249. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26881717 Review.
-
Systems biology based drug repositioning for development of cancer therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Jan;68:47-58. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.09.020. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 31568815 Review.
Cited by
-
Levofloxacin reposition-based design: synthesis, biological evaluation of new levofloxacin derivatives targeting topoisomerase II beta polymerase as promising anticancer agents, molecular docking, and physicochemical characterization.RSC Adv. 2024 Sep 3;14(38):28098-28119. doi: 10.1039/d4ra03975k. eCollection 2024 Aug 29. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39228758 Free PMC article.
-
Looking beyond the hype: Applied AI and machine learning in translational medicine.EBioMedicine. 2019 Sep;47:607-615. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.08.027. Epub 2019 Aug 26. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31466916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathway-Based Drug-Repurposing Schemes in Cancer: The Role of Translational Bioinformatics.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 14;10:605680. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.605680. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33520715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Genome-Wide Screening and Systems Biology Approaches in Drug Repositioning.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 21;12(9):2694. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092694. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32967266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative analysis of loss-of-function variants in clinical and genomic data reveals novel genes associated with cardiovascular traits.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 Jul 25;12(Suppl 6):108. doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0542-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31345219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lyman GH, Moses HL.. Biomarker tests for molecularly targeted therapies–the key to unlocking precision medicine. N Engl J Med 2016;375:4–6. - PubMed
-
- Mirnezami R, Nicholson J, Darzi A.. Preparing for precision medicine. N Engl J Med 2012;366:489–91. - PubMed
-
- Shameer K, Readhead B, Dudley JT.. Computational and experimental advances in drug repositioning for accelerated therapeutic stratification. Curr Top Med Chem 2015;15:5–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

