Behind the lines-actions of bacterial type III effector proteins in plant cells
- PMID: 28201715
- PMCID: PMC5091034
- DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuw026
Behind the lines-actions of bacterial type III effector proteins in plant cells
Abstract
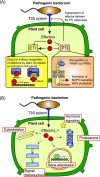
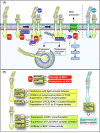
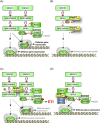
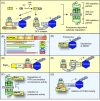
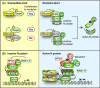
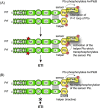
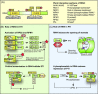
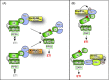
Pathogenicity of most Gram-negative plant-pathogenic bacteria depends on the type III secretion (T3S) system, which translocates bacterial effector proteins into plant cells. Type III effectors modulate plant cellular pathways to the benefit of the pathogen and promote bacterial multiplication. One major virulence function of type III effectors is the suppression of plant innate immunity, which is triggered upon recognition of pathogen-derived molecular patterns by plant receptor proteins. Type III effectors also interfere with additional plant cellular processes including proteasome-dependent protein degradation, phytohormone signaling, the formation of the cytoskeleton, vesicle transport and gene expression. This review summarizes our current knowledge on the molecular functions of type III effector proteins with known plant target molecules. Furthermore, plant defense strategies for the detection of effector protein activities or effector-triggered alterations in plant targets are discussed.
Keywords: type III effector; plant immunity; MAPK signaling; proteasome; cytoskeleton; phytohormones.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

