Chemotherapy for primary mediastinal yolk sac tumor in a patient undergoing chronic hemodialysis: a case report
- PMID: 28202048
- PMCID: PMC5312436
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-017-1213-7
Chemotherapy for primary mediastinal yolk sac tumor in a patient undergoing chronic hemodialysis: a case report
Abstract
Background: The safety and efficacy of chemotherapy for patients undergoing concomitant hemodialysis have not been fully established and optimal doses of anti-cancer drugs and best timing of hemodialysis remains unclear. Although chemosensitive cancers, such as germ cell tumors, treated with chemotherapy should have sufficient dose intensity maintained to achieve the desired effect, many patients with cancer undergoing hemodialysis might be under-treated because the pharmacokinetics of anti-cancer drugs in such patients remains unknown.
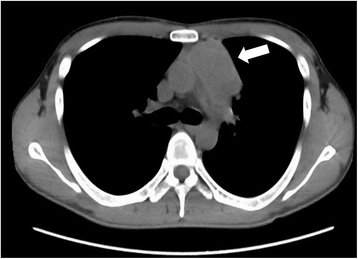
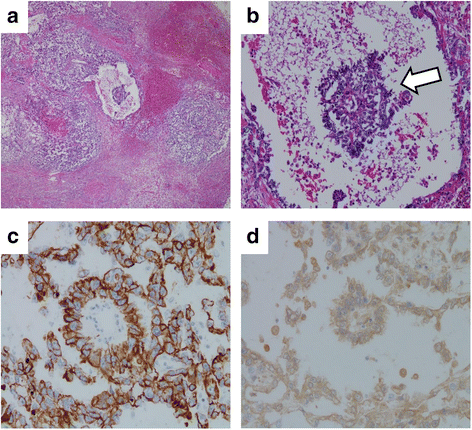
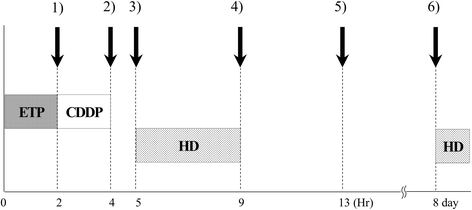
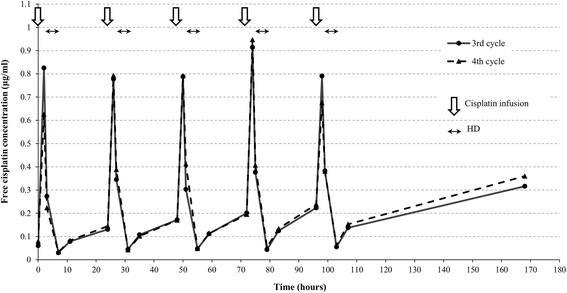
Case presentation: We describe a 31-year-old Japanese man with a mediastinal yolk sac tumor treated with surgery followed by five cycles of chemotherapy containing cisplatin and etoposide while concomitantly undergoing hemodialysis. The doses of these agents used in the first cycle were 50% of the standard dose of cisplatin (10 mg/m2) and 60% of the standard dose of etoposide (60 mg/m2) on days 1 through to 5; the doses were subsequently escalated to 75% with both agents. Hemodialysis was started 1 hour after infusions of these agents. Severe hematological toxicities were observed despite successful treatment. During treatment with concurrent hemodialysis, pharmacokinetic analysis of cisplatin was performed and its relationship with adverse effects was assessed. Compared with patients with normal renal function, the maximum drug concentration was higher, and concentration increased in the interval between hemodialysis and the subsequent cisplatin infusion, resulting in a higher area under the curve despite a reduction in the dose to 75% of the standard regimen.
Conclusions: Because of the altered pharmacokinetics pharmacodynamics status of patients with renal dysfunction undergoing hemodialysis, pharmacokinetics pharmacodynamics analysis is deemed to be helpful for effective and safe management of chemotherapy in patients undergoing hemodialysis.
Keywords: Cisplatin; Hemodialysis; Mediastinal yolk sac tumor; Pharmacokinetics; Renal insufficiency.
Figures
References
-
- Dehner LP. Germ cell tumors of the mediastinum. Germ cell tumors of the mediastinum. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990;7:266–84. - PubMed
-
- International Germ Cell Cancer Collaborative Group International Germ Cell Consensus Classification: a prognostic factor-based staging system for metastatic germ cell cancers. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:594–603. - PubMed
-
- Schmoll HJ, Souchon R, Krege S, Albers P, Beyer J, Kollmannsberger C, European Germ Cell Cancer Consensus Group et al. European consensus on diagnosis and treatment of germ cell cancer: a report of the European Germ Cell Cancer Consensus Group (EGCCCG) Ann Oncol. 2004;15:1377–99. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdh301. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Albany C, Einhorn LH. Extragonadal germ cell tumors: clinical presentation and management. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013;25:261–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

