Improvement of memory and learning by intracerebroventricular microinjection of T3 in rat model of ischemic brain stroke mediated by upregulation of BDNF and GDNF in CA1 hippocampal region
- PMID: 28202057
- PMCID: PMC5312580
- DOI: 10.1186/s40199-017-0169-x
Improvement of memory and learning by intracerebroventricular microinjection of T3 in rat model of ischemic brain stroke mediated by upregulation of BDNF and GDNF in CA1 hippocampal region
Abstract
Background: Ischemic stroke is a common leading cause of death and disability with lack of effective therapies. In this study, T3 was intra-ventricularly injected to evaluate gene expression and protein concentration of and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in hippocampal CA1 region in rat model of brain ischemia/reperfusion (I/R).
Methods: In this study, transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAo) was used as model of ischemic brain stroke. Rats were randomly divided in four groups of Co, Sh, tMCAo and tMCAo + T3. Then, a single dose of intra-ventricular T3 was administered via a Hamilton syringe. Passive avoidance test was used as behavioral investigations. After 21 days, the animals were sacrificed and their brains were used for molecular and histopathological studies.
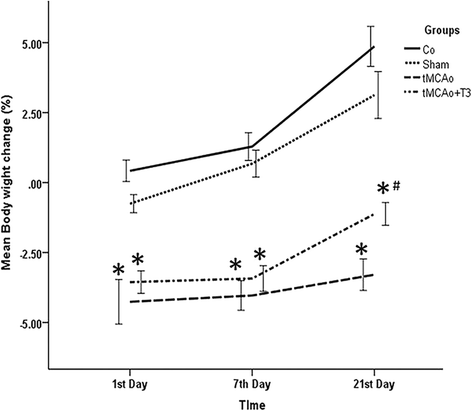
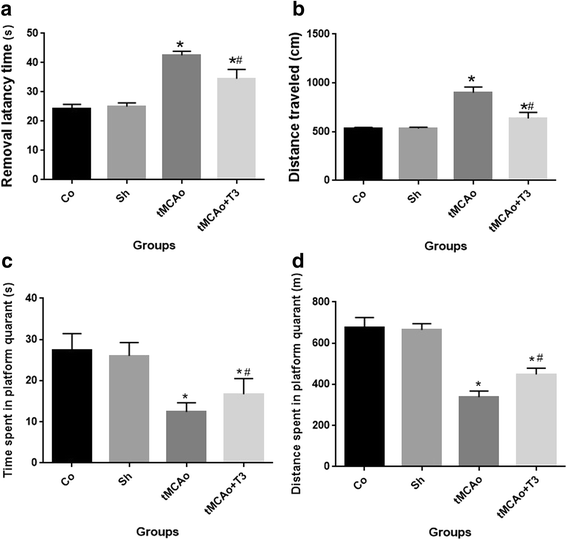
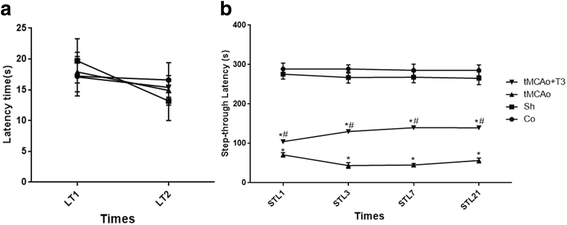
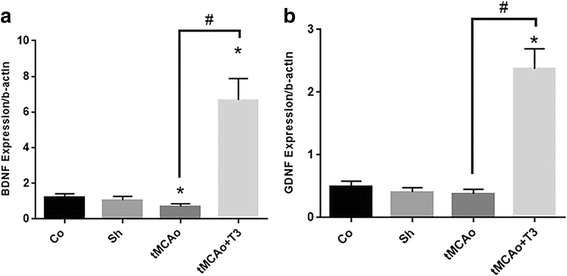
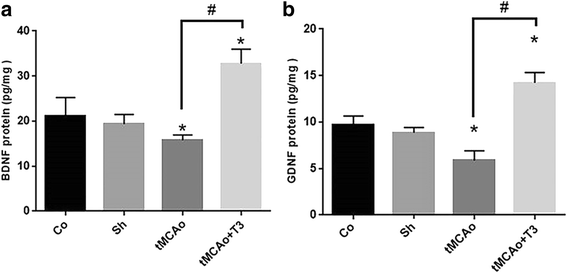
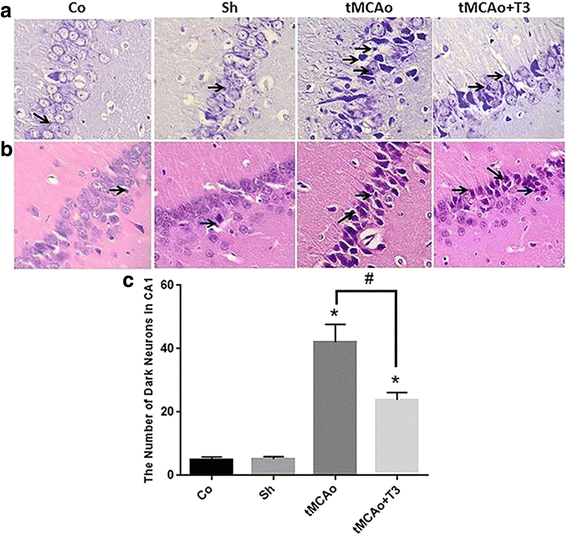
Results: T3 significantly improved the learning and memory compared with tMCAo group according to Morris water maze findings (P < 0.05). Step-through latency (STL) significantly decreased in tMCAo group (P < 0.05). There were significant increase in the STL of T3 group compared with tMCAo group (P < 0.05).A significant reduction in BDNF mRNAs and protein levels were observed in the tMCAo compared with Co and Sh group (P < 0.05). A significant increase of BDNF and GDNF mRNAs and proteins was recorded in tMCAo + T3 group compared with Co, Sh and tMCAO groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: The results of current study demonstrated that T3 had therapeutic effects on cerebral ischemic stroke by increasing the neurotrophic factors (BDNF, GDNF) in CA1 region of hippocampus. The effects of intracerebroventricular microinjection of T3on memory and learning in rat model of ischemic brain stroke.
Keywords: BDNF; CA1; GDNF; Stroke; Triiodothyronine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Neuroprotective Effects of Flaxseed Oil Supplementation on Functional Motor Recovery in a Model of Ischemic Brain Stroke: Upregulation of BDNF and GDNF.Acta Med Iran. 2017 Dec;55(12):785-792. Acta Med Iran. 2017. PMID: 29373886
-
Dopamine receptor activation increases glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in experimental stroke.Exp Neurol. 2013 Sep;247:202-8. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.04.016. Epub 2013 May 9. Exp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23664961
-
Retinoic acid-pretreated Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells in combination with triiodothyronine improve expression of neurotrophic factors in the subventricular zone of the rat ischemic brain injury.Metab Brain Dis. 2017 Feb;32(1):185-193. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9897-8. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Metab Brain Dis. 2017. PMID: 27549229
-
Recent Progress in Therapeutic Strategies for Ischemic Stroke.Cell Transplant. 2016;25(5):893-8. doi: 10.3727/096368916X690548. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Cell Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26786838 Review.
-
Neurotrophic Factors (BDNF and GDNF) and the Serotonergic System of the Brain.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2017 Mar;82(3):308-317. doi: 10.1134/S0006297917030099. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2017. PMID: 28320272 Review.
Cited by
-
The Flavone Luteolin Improves Central Nervous System Disorders by Different Mechanisms: A Review.J Mol Neurosci. 2018 Aug;65(4):491-506. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1094-2. Epub 2018 Aug 6. J Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30083786 Review.
-
Luteolin reversed anxiety and depressive-like behavior via modulation of the NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis in the hippocampus of rats subjected to sleep deprivation.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(8):1050-1058. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.75068.16277. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38911248 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular and Neuronal Consequences of Thyroid Hormones Alterations in the Ischemic Stroke.Metabolites. 2022 Dec 23;13(1):22. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010022. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36676947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of thyroid hormones in acute ischemic stroke - a meta analysis.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 24;7(1):16256. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16564-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29176727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid hormones and neurological impairments during the first two days after stroke: A pilot study.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 11;11(2):e41921. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41921. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39897873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black JM, Hawks JH, Keene AM. Medical-surgical nursing: Clinical management for positive outcomes. 2005.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

