Alternative transmission routes in the malaria elimination era: an overview of transfusion-transmitted malaria in the Americas
- PMID: 28202065
- PMCID: PMC5312538
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-017-1726-y
Alternative transmission routes in the malaria elimination era: an overview of transfusion-transmitted malaria in the Americas
Abstract
Background: Transfusion-transmitted (TT) malaria is an alternative infection route that has gained little attention from authorities, despite representing a life-threatening condition. There has been no systematic review of this health problem in American countries. The aim of this study was to describe the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of TT malaria in the Americas and identify factors associated with lethality based on the studies published in the literature.
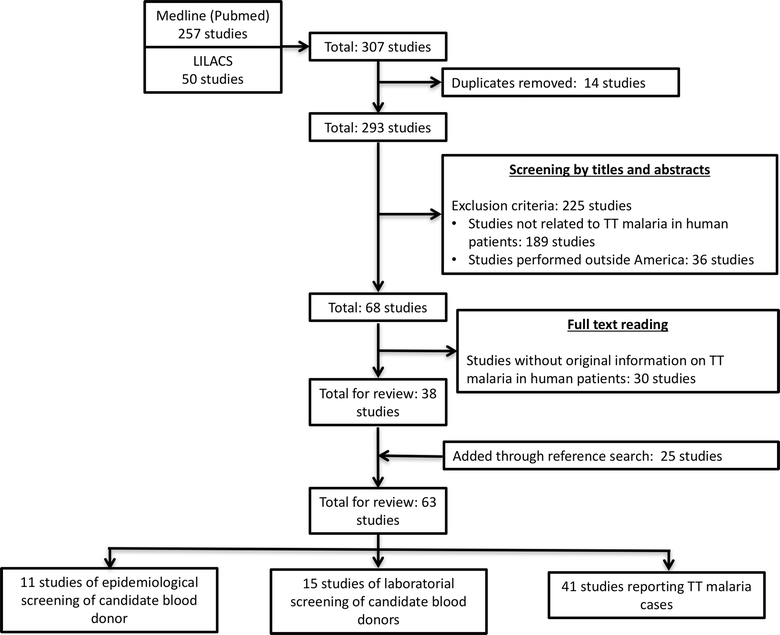
Methods: Potentially relevant papers in all languages were retrieved from MEDLINE and LILACS. Additional articles were obtained from reviews and original papers. Publications on screening of candidate blood donors and on surveillance of TT malaria cases were included. Odds ratios with respective 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated. Epidemiological characteristics of blood donors of TT malaria cases, including a pooled positivity of different tests for malaria diagnosis, were retrieved.
Results: A total of 63 publications regarding TT malaria from seven countries were included, from 1971 to 2016. A total of 422 cases of TT malaria were recorded. Most TT malaria cases were in females (62.0%) and 39.5% were in the ≥61 years-old age group. About half of all cases were from Mexico (50.7%), 40.3% from the United States of America (USA) and 6.6% from Brazil. Gyneco-obstetrical conditions (67.3%), surgical procedures (20.6%) and complications from neoplasias (6.1%) were the most common indications of transfusion. Packed red blood cells (RBCs) (50.7%) and whole blood (43.3%) were the blood products mostly associated with TT malaria. Cases were mostly caused by Plasmodium malariae (58.4%), followed by Plasmodium vivax (20.7%) and Plasmodium falciparum (17.9%). A total of 66.6% of cases were diagnosed by microscopy. Incubation period of 2-3 weeks was the most commonly observed (28.6%). Lethality was seen in 5.3% of cases and was associated with living in non-endemic countries, P. falciparum infection and concomitant neoplastic diseases.
Conclusion: There is an important research and knowledge gap regarding the TT malaria burden in Latin American countries where malaria remains endemic. No screening method that is practical, affordable and suitably sensitive is available at blood banks in Latin American countries, where infections with low parasitaemia contribute greatly to transmission. Lethality from TT malaria was not negligible. TT malaria needs to be acknowledged and addressed in areas moving toward elimination.
Keywords: Blood transfusion; Malaria; Plasmodium; Transfusion-transmitted malaria.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . World malaria report 2015. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous