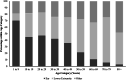
Vibrio alginolyticus infections in the USA, 1988-2012
- PMID: 28202099
- PMCID: PMC9203320
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268817000140
Vibrio alginolyticus infections in the USA, 1988-2012
Abstract
Vibrio alginolyticus causes soft tissue and bloodstream infection; little systematically collected clinical and epidemiological information is available. In the USA, V. alginolyticus infections are reported to the Cholera and Other Vibrio Illness Surveillance system. Using data from 1988 to 2012, we categorised infections using specimen source and exposure history, analysed case characteristics, and calculated incidence rates using US Census Bureau data. Most (96%) of the 1331 V. alginolyticus infections were from coastal states. Infections of the skin and ear were most frequent (87%); ear infections occurred more commonly in children, lower extremity infections more commonly in older adults. Most (86%) infections involved water activity. Reported incidence of infections increased 12-fold over the study period, although the extent of diagnostic or surveillance bias is unclear. Prevention efforts should target waterborne transmission in coastal areas and provider education to promote more rapid diagnosis and prevent complications.
Keywords: Vibrio alginolyticus; ear infection; skin and soft tissue infection; surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Daniels NA, et al. Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections in the United States, 1973–1998. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2000; 181: 1661–1666. - PubMed
-
- Horseman MA, Surani S. A comprehensive review of Vibrio vulnificus: an important cause of severe sepsis and skin and soft-tissue infection. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2011; 15: e157–e166. - PubMed
-
- Pickering LK, Peter G, Shulman ST. The Red Book through the ages. Pediatrics 2013; 132: 898–906. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources