PARPs and ADP-ribosylation: recent advances linking molecular functions to biological outcomes
- PMID: 28202539
- PMCID: PMC5322727
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.291518.116
PARPs and ADP-ribosylation: recent advances linking molecular functions to biological outcomes
Abstract
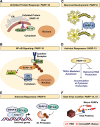
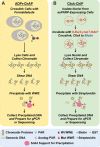
The discovery of poly(ADP-ribose) >50 years ago opened a new field, leading the way for the discovery of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) family of enzymes and the ADP-ribosylation reactions that they catalyze. Although the field was initially focused primarily on the biochemistry and molecular biology of PARP-1 in DNA damage detection and repair, the mechanistic and functional understanding of the role of PARPs in different biological processes has grown considerably of late. This has been accompanied by a shift of focus from enzymology to a search for substrates as well as the first attempts to determine the functional consequences of site-specific ADP-ribosylation on those substrates. Supporting these advances is a host of methodological approaches from chemical biology, proteomics, genomics, cell biology, and genetics that have propelled new discoveries in the field. New findings on the diverse roles of PARPs in chromatin regulation, transcription, RNA biology, and DNA repair have been complemented by recent advances that link ADP-ribosylation to stress responses, metabolism, viral infections, and cancer. These studies have begun to reveal the promising ways in which PARPs may be targeted therapeutically for the treatment of disease. In this review, we discuss these topics and relate them to the future directions of the field.
Keywords: DNA repair; RNA biology; gene regulation; mono(ADP-ribose) (MAR); poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR); poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP).
© 2017 Gupte et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



References
-
- Adhya D, Basu A. 2010. Epigenetic modulation of host: new insights into immune evasion by viruses. J Biosci 35: 647–663. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Quesada R, Munoz-Gamez JA, Martin-Oliva D, Peralta A, Valenzuela MT, Matinez-Romero R, Quiles-Perez R, Menissier-de Murcia J, de Murcia G, Ruiz de Almodovar M, et al. 2007. Interaction between ATM and PARP-1 in response to DNA damage and sensitization of ATM deficient cells through PARP inhibition. BMC Mol Biol 8: 29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahel I, Ahel D, Matsusaka T, Clark AJ, Pines J, Boulton SJ, West SC. 2008. Poly(ADP-ribose)-binding zinc finger motifs in DNA repair/checkpoint proteins. Nature 451: 81–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
