AAV-mediated delivery of optogenetic constructs to the macaque brain triggers humoral immune responses
- PMID: 28202570
- PMCID: PMC5411474
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00780.2016
AAV-mediated delivery of optogenetic constructs to the macaque brain triggers humoral immune responses
Abstract
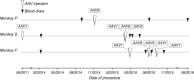
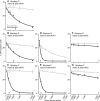
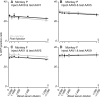
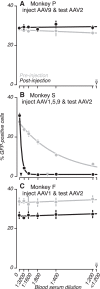
Gene delivery to the primate central nervous system via recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors (AAV) allows neurophysiologists to control and observe neural activity precisely. A current limitation of this approach is variability in vector transduction efficiency. Low levels of transduction can foil experimental manipulations, prompting vector readministration. The ability to make multiple vector injections into the same animal, even in cases where successful vector transduction has already been achieved, is also desirable. However, vector readministration has consequences for humoral immunity and gene delivery that depend on vector dosage and route of administration in complex ways. As part of optogenetic experiments in rhesus monkeys, we analyzed blood sera collected before and after AAV injections into the brain and quantified neutralizing antibodies to AAV using an in vitro assay. We found that injections of AAV1 and AAV9 vectors elevated neutralizing antibody titers consistently. These immune responses were specific to the serotype injected and were long lasting. These results demonstrate that optogenetic manipulations in monkeys trigger immune responses to AAV capsids, suggesting that vector readministration may have a higher likelihood of success by avoiding serotypes injected previously.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Adeno-associated viral vector (AAV)-mediated gene delivery is a valuable tool for neurophysiology, but variability in transduction efficiency remains a bottleneck for experimental success. Repeated vector injections can help overcome this limitation but affect humoral immune state and transgene expression in ways that are poorly understood. We show that AAV vector injections into the primate central nervous system trigger long-lasting and serotype-specific immune responses, raising the possibility that switching serotypes may promote successful vector readministration.
Keywords: AAV vectors; neutralizing antibodies; nonhuman primate; optogenetics.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibody neutralization poses a barrier to intravitreal adeno-associated viral vector gene delivery to non-human primates.Gene Ther. 2015 Feb;22(2):116-26. doi: 10.1038/gt.2014.115. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Gene Ther. 2015. PMID: 25503696 Free PMC article.
-
Intramuscular administration of AAV overcomes pre-existing neutralizing antibodies in rhesus macaques.Vaccine. 2016 Dec 7;34(50):6323-6329. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.10.053. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27817961
-
Mapping an Adeno-associated Virus 9-Specific Neutralizing Epitope To Develop Next-Generation Gene Delivery Vectors.J Virol. 2018 Sep 26;92(20):e01011-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01011-18. Print 2018 Oct 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30089698 Free PMC article.
-
AAV Vector Immunogenicity in Humans: A Long Journey to Successful Gene Transfer.Mol Ther. 2020 Mar 4;28(3):723-746. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.12.010. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31972133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pre-existing anti-adeno-associated virus antibodies as a challenge in AAV gene therapy.Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2013 Apr;24(2):59-67. doi: 10.1089/hgtb.2012.243. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2013. PMID: 23442094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene delivery to neurons in the auditory brainstem of barn owls using standard recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors.Curr Res Neurobiol. 2020 Aug 6;1:100001. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2020.100001. eCollection 2020 Dec. Curr Res Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 36249276 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of chemogenetics in non-human primates.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2022 Jun;64:102204. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2022.102204. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35307295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemogenetic Inhibition of the Amygdala Modulates Emotional Behavior Expression in Infant Rhesus Monkeys.eNeuro. 2019 Oct 14;6(5):ENEURO.0360-19.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0360-19.2019. Print 2019 Sep/Oct. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 31541000 Free PMC article.
-
Development of optically controlled "living electrodes" with long-projecting axon tracts for a synaptic brain-machine interface.Sci Adv. 2021 Jan 22;7(4):eaay5347. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay5347. Print 2021 Jan. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33523957 Free PMC article.
-
New era of optogenetics: from the central to peripheral nervous system.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Feb;55(1):1-16. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2020.1726279. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32070147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blacklow NR, Hoggan MD, Rowe WP. Serologic evidence for human infection with adenovirus-associated viruses. J Natl Cancer Inst 40: 319–327, 1968. - PubMed
-
- Bordet J, Gengou O. Sur l’existence de substances sensibilisatrices dans la plupart des sérums antimicrobiens. Ann Inst Pasteur 15: 289–302, 1901.
-
- Calcedo R, Franco J, Qin Q, Richardson DW, Mason JB, Boyd S, Wilson JM. Preexisting neutralizing antibodies to adeno-associated virus capsids in large animals other than monkeys may confound in vivo gene therapy studies. Hum Gene Ther Methods 26: 103–105, 2015. doi:10.1089/hgtb.2015.082. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

