DNA Repair Interacts with Autophagy To Regulate Inflammatory Responses to Pulmonary Hyperoxia
- PMID: 28202616
- PMCID: PMC5360514
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601001
DNA Repair Interacts with Autophagy To Regulate Inflammatory Responses to Pulmonary Hyperoxia
Erratum in
-
Correction: DNA Repair Interacts with Autophagy To Regulate Inflammatory Responses to Pulmonary Hyperoxia.J Immunol. 2017 Aug 1;199(3):1207. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700711. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28739596 No abstract available.
Abstract
Oxygen is supplied as a supportive treatment for patients suffering from acute respiratory distress syndrome. Unfortunately, high oxygen concentration increases reactive oxygen species generation, which causes DNA damage and ultimately cell death in the lung. Although 8-oxoguanine-DNA glycosylase (OGG-1) is involved in repairing hyperoxia-mediated DNA damage, the underlying molecular mechanism remains elusive. In this study, we report that ogg-1-deficient mice exhibited a significant increase of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ) in the lung after being exposed to 95% oxygen. In addition, we found that ogg-1 deficiency downregulated (macro)autophagy when exposed to hyperoxia both in vitro and in vivo, which was evident by decreased conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II, reduced LC3 punctate staining, and lower Atg7 expression compared with controls. Using a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, we found that OGG-1 associated with the promoter of Atg7, suggesting a role for OGG1 in regulation of Atg7 activity. Knocking down OGG-1 decreased the luciferase reporter activity of Atg7. Further, inflammatory cytokine levels in murine lung epithelial cell line cells were downregulated following autophagy induction by starvation and rapamycin treatment, and upregulated when autophagy was blocked using 3-methyladenine and chloroquine. atg7 knockout mice and Atg7 small interfering RNA-treated cells exhibited elevated levels of phospho-NF-κB and intensified inflammatory cytokines, suggesting that Atg7 impacts inflammatory responses to hyperoxia. These findings demonstrate that OGG-1 negatively regulates inflammatory cytokine release by coordinating molecular interaction with the autophagic pathway in hyperoxia-induced lung injury.
Copyright © 2017 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

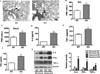


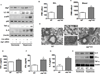

Comment in
-
Comment on "DNA Repair Interacts with Autophagy To Regulate Inflammatory Responses to Pulmonary Hyperoxia".J Immunol. 2017 Jul 15;199(2):381. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700591. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28696326 No abstract available.
-
Response to Comment on "DNA Repair Interacts with Autophagy To Regulate Inflammatory Responses to Pulmonary Hyperoxia".J Immunol. 2017 Jul 15;199(2):381-382. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700676. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28696327 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chiu WH, Luo SJ, Chen CL, Cheng JH, Hsieh CY, Wang CY, Huang WC, Su WC, Lin CF. Vinca alkaloids cause aberrant ROS-mediated JNK activation, Mcl-1 downregulation, DNA damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:1159–1171. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho CR, Schettino G, de Paula Pinto Maranhao B, Bethlem EP. Hyperoxia and lung disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 1998;4:300–304. - PubMed
-
- Barazzone C, White CW. Mechanisms of cell injury and death in hyperoxia: role of cytokines and Bcl-2 family proteins. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2000;22:517–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

