Central Role of Metabolism in Endothelial Cell Function and Vascular Disease
- PMID: 28202623
- PMCID: PMC5337830
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00031.2016
Central Role of Metabolism in Endothelial Cell Function and Vascular Disease
Abstract
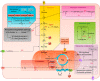
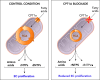
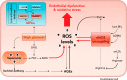
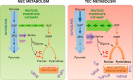
The importance of endothelial cell (EC) metabolism and its regulatory role in the angiogenic behavior of ECs during vessel formation and in the function of different EC subtypes determined by different vascular beds has been recognized only in the last few years. Even more importantly, apart from a role of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in EC dysfunction, deregulations of EC metabolism in disease only recently received increasing attention. Although comprehensive metabolic characterization of ECs still needs further investigation, the concept of targeting EC metabolism to treat vascular disease is emerging. In this overview, we summarize EC-specific metabolic pathways, describe the current knowledge on their deregulation in vascular diseases, and give an outlook on how vascular endothelial metabolism can serve as a target to normalize deregulated endothelium.
©2017 Int. Union Physiol. Sci./Am. Physiol. Soc.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures
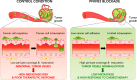
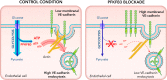
References
-
- Aiello LP, Avery RL, Arrigg PG, Keyt BA, Jampel HD, Shah ST, Pasquale LR, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N Engl J Med 331: 1480–1487, 1994. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC. Endothelium as an organ system. Crit Care Med 32: S271–S279, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res 100: 158–173, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Anggard EE. The endothelium: the body's largest endocrine gland? J Endocrinol 127: 371–375, 1990. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

