Targeting PAK1
- PMID: 28202661
- PMCID: PMC5973817
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20160134
Targeting PAK1
Abstract
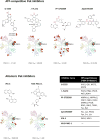
p21-Activated kinase 1 (PAK1) has attracted much attention as a potential therapeutic target due to its central role in many oncogenic signaling pathways, its frequent dysregulation in cancers and neurological disorders, and its tractability as a target for small-molecule inhibition. To date, several PAK1-targeting compounds have been developed as preclinical agents, including one that has been evaluated in a clinical trial. A series of ATP-competitive inhibitors, allosteric inhibitors and peptide inhibitors with distinct biochemical and pharmacokinetic properties represent useful laboratory tools for studies on the role of PAK1 in biology and in disease contexts, and could lead to promising therapeutic agents. Given the central role of PAK1 in vital signaling pathways, future clinical development of PAK1 inhibitors will require careful investigation of their safety and efficacy.
Keywords: cancer; protein–serine–threonine kinases; signaling; small molecules; therapeutics.
© 2017 The Author(s); published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibitors of p21-activated kinases (PAKs).J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 8;58(1):111-29. doi: 10.1021/jm501613q. Epub 2014 Dec 3. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25415869
-
Molecular pathways: targeting p21-activated kinase 1 signaling in cancer--opportunities, challenges, and limitations.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jul 15;18(14):3743-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1952. Epub 2012 May 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22595609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P21-Activated Kinase 1: Emerging biological functions and potential therapeutic targets in Cancer.Theranostics. 2020 Aug 1;10(21):9741-9766. doi: 10.7150/thno.46913. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32863957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating PAK1: Accessory Proteins as Promising Therapeutic Targets.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 7;15(2):242. doi: 10.3390/biom15020242. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) to induce apoptosis of tumor cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Apr 26;108(17):7177-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103350108. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21482786 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
RHO Family GTPases in the Biology of Lymphoma.Cells. 2019 Jun 26;8(7):646. doi: 10.3390/cells8070646. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31248017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Agonist Effects of Propranolol on Non-Tumor Human Breast Cells.Cells. 2020 Apr 22;9(4):1036. doi: 10.3390/cells9041036. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32331276 Free PMC article.
-
Proteogenomic characterization of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Cell. 2021 Sep 16;184(19):5031-5052.e26. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.08.023. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34534465 Free PMC article.
-
Interrogation of kinase genetic interactions provides a global view of PAK1-mediated signal transduction pathways.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 11;295(50):16906-16919. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014831. Epub 2020 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33060198 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Signaling by Small GTPases in Metastatic Disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 21;10:841572. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.841572. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35127690 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sells MA, Knaus UG, Bagrodia S, Ambrose DM, Bokoch GM, Chernoff J. Human p21-activated kinase (Pak1) regulates actin organization in mammalian cells. Curr Biol. 1997;7:202–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

