Systemic delivery of factor IX messenger RNA for protein replacement therapy
- PMID: 28202722
- PMCID: PMC5347596
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1619653114
Systemic delivery of factor IX messenger RNA for protein replacement therapy
Abstract
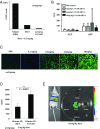
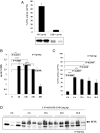
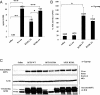
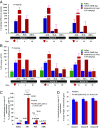
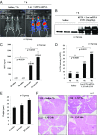
Safe and efficient delivery of messenger RNAs for protein replacement therapies offers great promise but remains challenging. In this report, we demonstrate systemic, in vivo, nonviral mRNA delivery through lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to treat a Factor IX (FIX)-deficient mouse model of hemophilia B. Delivery of human FIX (hFIX) mRNA encapsulated in our LUNAR LNPs results in a rapid pulse of FIX protein (within 4-6 h) that remains stable for up to 4-6 d and is therapeutically effective, like the recombinant human factor IX protein (rhFIX) that is the current standard of care. Extensive cytokine and liver enzyme profiling showed that repeated administration of the mRNA-LUNAR complex does not cause any adverse innate or adaptive immune responses in immune-competent, hemophilic mice. The levels of hFIX protein that were produced also remained consistent during repeated administrations. These results suggest that delivery of long mRNAs is a viable therapeutic alternative for many clotting disorders and for other hepatic diseases where recombinant proteins may be unaffordable or unsuitable.
Keywords: hemophilia B therapy; hepatic diseases; lipid nanoparticles; nonviral mRNA delivery; systemic delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sahin U, Karikó K, Türeci Ö. mRNA-based therapeutics: Developing a new class of drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13(10):759–780. - PubMed
-
- Yin H, et al. Non-viral vectors for gene-based therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(8):541–555. - PubMed
-
- Jirikowski GF, Sanna PP, Maciejewski-Lenoir D, Bloom FE. Reversal of diabetes insipidus in Brattleboro rats: Intrahypothalamic injection of vasopressin mRNA. Science. 1992;255(5047):996–998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

