Black Cohosh Hepatotoxicity with Autoimmune Hepatitis Presentation
- PMID: 28203134
- PMCID: PMC5301124
- DOI: 10.1159/000452735
Black Cohosh Hepatotoxicity with Autoimmune Hepatitis Presentation
Abstract
Herbal medicines have been used for the treatment of various ailments since time immemorial. Black cohosh (BC) is well known for the treatment of postmenopausal symptoms, with conflicting evidence supporting its safety and benefits. We present a rare case of BC-induced autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) with hepatotoxicity in a 69-year-old female. To our knowledge, this represents the third case of BC-induced AIH.
Keywords: Autoimmune hepatitis presentation; Black cohosh; Hepatotoxicity.
Figures

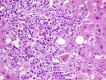
Similar articles
-
Liver Injury with Features Mimicking Autoimmune Hepatitis following the Use of Black Cohosh.Case Rep Med. 2009;2009:918156. doi: 10.1155/2009/918156. Epub 2010 Jan 10. Case Rep Med. 2009. PMID: 20130783 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous reports of assumed herbal hepatotoxicity by black cohosh: is the liver-unspecific Naranjo scale precise enough to ascertain causality?Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011 Jun;20(6):567-82. doi: 10.1002/pds.2127. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011. PMID: 21702069
-
Suspected hepatotoxicity by Cimicifugae racemosae rhizoma (black cohosh, root): critical analysis and structured causality assessment.Phytomedicine. 2009 Jan;16(1):72-84. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2008.09.009. Epub 2008 Nov 17. Phytomedicine. 2009. PMID: 19010650
-
Black cohosh hepatotoxicity: quantitative causality evaluation in nine suspected cases.Menopause. 2009 Sep-Oct;16(5):956-65. doi: 10.1097/GME.0b013e31819d3904. Menopause. 2009. PMID: 19339903 Review.
-
United States Pharmacopeia review of the black cohosh case reports of hepatotoxicity.Menopause. 2008 Jul-Aug;15(4 Pt 1):628-38. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e31816054bf. Menopause. 2008. PMID: 18340277 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of biological therapies in autoimmune hepatitis: A case-based systematic review.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2025 Mar 22;16(1):101481. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v16.i1.101481. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2025. PMID: 40123748 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of steroidogenesis by Actaea racemosa and vitamin C combination, in letrozole induced polycystic ovarian syndrome rat model: promising activity without the risk of hepatic adverse effect.Chin Med. 2021 Apr 29;16(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00444-z. Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 33926485 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatotoxicity of Herbal Supplements Mediated by Modulation of Cytochrome P450.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 8;18(11):2353. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112353. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29117101 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lontos S, Jones RM, Angus PW, Gow PJ. Acute liver failure associated with the use of herbal preparations containing black cohosh. Med J Aust. 2003;179:390–391. - PubMed
-
- Pierard S, Coche JC, Lanthier P, Dekoninck X, Lanthier N, Rahier J, Geubel AP. Severe hepatitis associated with the use of black cohosh: a report of two cases and an advice for caution. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;21:941–945. - PubMed
-
- Teschke R, Bahre R, Genthner A, Fuchs J, Schmidt-Taenzer W, Wolff A. Suspected black cohosh hepatotoxicity – challenges and pitfalls of causality assessment. Maturitas. 2009;63:302–314. - PubMed
-
- Nuntanakorn P, Jiang B, Einbond LS, Yang H, Kronenberg F, Weinstein IB, Kennelly EJ. Polyphenolic constituents of Actaea racemosa. J Nat Prod. 2006;69:314–318. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

