Tamoxifen Activation of Cre-Recombinase Has No Persisting Effects on Adult Neurogenesis or Learning and Anxiety
- PMID: 28203140
- PMCID: PMC5285339
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00027
Tamoxifen Activation of Cre-Recombinase Has No Persisting Effects on Adult Neurogenesis or Learning and Anxiety
Abstract
Adult neurogenesis is a tightly regulated process continuously taking place in the central nervous system of most mammalian species. In neuroscience research, transgenic animals bearing the tamoxifen-inducible CreERT2-Lox system are widely used. In this study, we made use of a Nestin-CreERT2/R26R-YFP transgenic mouse model in which the CreERT2 activates the expression of YFP in multipotent neural stem cells upon tamoxifen application. Humoral factors, such as the levels of estrogens, have been reported to affect the hippocampal neurogenesis. The application of tamoxifen, a mixed agonist/antagonist of the estrogen receptor that permeates the blood-brain-barrier, could thus influence adult neurogenesis. Although the functions of adult neurogenesis are yet to be fully deciphered, a reciprocal interaction between rates of neurogenesis on the one hand and learning and mood regulation on the other hand, has been suggested. The impact of tamoxifen on neurogenesis and behavior was therefore addressed following five daily applications according to the open field test, the elevated plus maze, and Morris water maze. In addition, the impact of short-term tamoxifen application on progenitor cell proliferation, morphology, and fate in the neurogenic niche of the dentate gyrus were investigated. Finally, the influence of the route of administration (oral vs. intra-peritoneal) and gender-specific response were scrutinized. The sub-acute analysis did neither reveal significant differences in behavior, such as voluntary motor activity, anxiety behavior, and spatial learning, nor in cell proliferation, cell survival, dendritic arborization or maturation rate within the dentate gyrus between saline solution-, corn oil-, and tamoxifen-treated groups. Finally, neither the route of application, nor the gender of treated mice influenced the response to tamoxifen. We conclude that short tamoxifen treatments used to activate the CreERT2 system in transgenic mouse models does not have a measurable impact on adult neurogenesis or the here tested behavior, and is therefore appropriate for most studies in the field.
Keywords: CreERT; behavior; gender; hippocampus; learning; memory; nestin; neurogenesis.
Figures

 , Open Field = □, Water Maze Learning = Ⓛ, and Water Maze Memory = Ⓜ) were performed from day 8 to 12. Mice were perfused on day 15. (B) Total distance covered in the open field test shows no significant differences in locomotion comparing corn oil and tamoxifen treatment groups. (C,D) The comparison of corn oil and tamoxifen treatment groups in the time spent in the open arm of the elevated plus maze and the number of entries in the open arms reveals no significant differences in levels of anxiety. The same result was observed by comparing the saline solution-treated group with either corn oil-treated or tamoxifen-treated mice (data not shown). (E,F) Gender-specific analysis of elevated plus maze data revealed significant differences in anxiety levels of females compared to males according to the time spent in open arms (p = 0.0065**) and number of open arm entries (p = 0.0465*). (G–I) Learning and memory performances were analyzed using the Morris water maze test. (G) Learning curve (time to find the platform) from day 8 to 12 revealed no learning differences between corn oil and tamoxifen treated mice, as analyzed by two-way ANOVA. Following removal of the platform on day 12, no differences in memory according (H) to the time spent in platform quadrant and (I) number of platform crossings were noticed between the tamoxifen and corn oil treated mice, as well as the saline-treated animals (data not shown).
, Open Field = □, Water Maze Learning = Ⓛ, and Water Maze Memory = Ⓜ) were performed from day 8 to 12. Mice were perfused on day 15. (B) Total distance covered in the open field test shows no significant differences in locomotion comparing corn oil and tamoxifen treatment groups. (C,D) The comparison of corn oil and tamoxifen treatment groups in the time spent in the open arm of the elevated plus maze and the number of entries in the open arms reveals no significant differences in levels of anxiety. The same result was observed by comparing the saline solution-treated group with either corn oil-treated or tamoxifen-treated mice (data not shown). (E,F) Gender-specific analysis of elevated plus maze data revealed significant differences in anxiety levels of females compared to males according to the time spent in open arms (p = 0.0065**) and number of open arm entries (p = 0.0465*). (G–I) Learning and memory performances were analyzed using the Morris water maze test. (G) Learning curve (time to find the platform) from day 8 to 12 revealed no learning differences between corn oil and tamoxifen treated mice, as analyzed by two-way ANOVA. Following removal of the platform on day 12, no differences in memory according (H) to the time spent in platform quadrant and (I) number of platform crossings were noticed between the tamoxifen and corn oil treated mice, as well as the saline-treated animals (data not shown).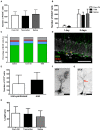
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

