Dopamine D1 Receptor Immunoreactivity on Fine Processes of GFAP-Positive Astrocytes in the Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata of Adult Mouse
- PMID: 28203148
- PMCID: PMC5285371
- DOI: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00003
Dopamine D1 Receptor Immunoreactivity on Fine Processes of GFAP-Positive Astrocytes in the Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata of Adult Mouse
Abstract
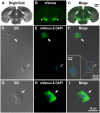
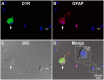
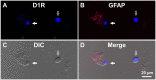
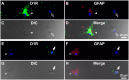
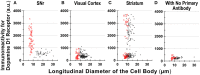
Substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr), the major output nucleus of the basal ganglia, receives dopamine from dendrites extending from dopaminergic neurons of the adjacent nucleus pars compacta (SNc), which is known for its selective degeneration in Parkinson's disease. As a recipient for dendritically released dopamine, the dopamine D1 receptor (D1R) is a primary candidate due to its very dense immunoreactivity in the SNr. However, the precise location of D1R remains unclear at the cellular level in the SNr except for that reported on axons/axon terminals of presumably striatal GABAergic neurons. To address this, we used D1R promotor-controlled, mVenus-expressing transgenic mice. When cells were acutely dissociated from SNr of mouse brain, prominent mVenus fluorescence was detected in fine processes of glia-like cells, but no such fluorescence was detected from neurons in the same preparation, except for the synaptic bouton-like structure on the neurons. Double immunolabeling of SNr cells dissociated from adult wild-type mice brain further revealed marked D1R immunoreactivity in the processes of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-positive astrocytes. Such D1R imunoreactivity was significantly stronger in the SNr astrocytes than that in those of the visual cortex in the same preparation. Interestingly, GFAP-positive astrocytes dissociated from the striatum demonstrated D1R immunoreactivity, either remarkable or minimal, similarly to that shown in neurons in this nucleus. In contrast, in the SNr and visual cortex, only weak D1R immunoreactivity was detected in the neurons tested. These results suggest that the SNr astrocyte may be a candidate recipient for dendritically released dopamine. Further study is required to fully elucidate the physiological roles of divergent dopamine receptor immunoreactivity profiles in GFAP-positive astrocytes.
Keywords: basal ganglia; dendritic release; glia; striatum; visual cortex.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

