Comparison of 2D (RANO) and volumetric methods for assessment of recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab-a report from the BELOB trial
- PMID: 28204639
- PMCID: PMC5464446
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/now311
Comparison of 2D (RANO) and volumetric methods for assessment of recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab-a report from the BELOB trial
Abstract
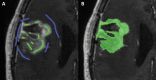
Background: The current method for assessing progressive disease (PD) in glioblastoma is according to the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria. Bevacizumab-treated patients may show pseudo-response on postcontrast T1-weighted (T1w) MRI, and a more infiltrative non-enhancing growth pattern on T2w/fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images. We investigated whether the RANO criteria remain the method of choice for assessing bevacizumab-treated recurrent glioblastoma when compared with various volumetric methods.
Methods: Patients with assessable MRI data from the BELOB trial (n = 148) were included. Patients were treated with bevacizumab, lomustine, or both. At first and second radiological follow-up (6 and 12 wk), PD was determined using the 2D RANO criteria and various volumetric methods based on enhancing tumor only and enhancing plus non-enhancing tumor. Differences in overall survival (OS) between PD and non-PD patients were assessed with the log-rank test and a Cox model. Hazard ratios (HRs) and their 95% CIs were determined.
Results: For all patients together, all methods (except subtraction of non-enhancing from enhancing volume at first follow-up) showed significant differences in OS between PD and non-PD patients (P < .001). The largest risk increase for death in case of PD at both first and second follow-up was found with the RANO criteria: HR = 2.81 (95% CI, 1.92-4.10) and HR = 2.80 (95% CI, 1.75-4.49), respectively. In the bevacizumab-treated patients, all methods assessed showed significant differences in OS between PD and non-PD patients. There were no significant differences between methods.
Conclusions: In the first 12 weeks, volumetric methods did not provide significant improvement over the RANO criteria as a posttreatment prognostic marker.
Keywords: RANO; bevacizumab; recurrent glioblastoma; volumetry.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures



Comment in
-
Response assessment in high-grade glioma: tumor volume as endpoint.Neuro Oncol. 2017 Jun 1;19(6):744-745. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox035. Neuro Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28379518 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al. ; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumour and Radiation Oncology Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(5):459–466. - PubMed
-
- Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, et al. Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(28):4733–4740. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science. 2005;307(5706):58–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

