EFFECTIVE DOSE PER UNIT KERMA-AREA PRODUCT CONVERSION FACTORS IN ADULTS UNDERGOING MODIFIED BARIUM SWALLOW STUDIES
- PMID: 28204745
- PMCID: PMC5927331
- DOI: 10.1093/rpd/ncx006
EFFECTIVE DOSE PER UNIT KERMA-AREA PRODUCT CONVERSION FACTORS IN ADULTS UNDERGOING MODIFIED BARIUM SWALLOW STUDIES
Abstract
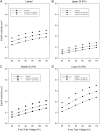
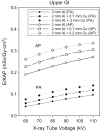
This study presents an investigation of adult effective dose (E) per unit Kerma-Area Product (KAP) in Modified Barium Swallow Study (MBSS) examinations. PC program for X-ray Monte Carlo (version 2.0.1) was used to calculate patient organ doses during MBSS examinations, which used combined to generate effective dose. Normalized patient doses were obtained by dividing the effective dose (mSv) by the incident KAP (Gy·cm2). Five standard projections were studied and the importance of X-ray beam size and in patient size (body mass index) were investigated. Lateral projections had an average E/KAP conversion factor of 0.19 ± 0.04 mSv/Gy·cm2. The average E/KAP was highest for upper gastrointestinal (GI) anterior-posterior projections (0.27 ± 0.04 mSv/Gy·cm2) and lowest for upper GI posterior-anterior projections (0.09 ± 0.03 mSv/Gy·cm2). E/KAP always increased with increasing filtration and/or X-ray tube voltage. Reducing the X-ray beam cross-sectional area increased the E/KAP conversion factors. Small patients have the E/KAP conversion factors that are twice those of a standard adult. Conversion factors for effective dose of adult patients undergoing MBSS examinations must account for X-ray beam projection, beam quality (kV and filtration), image size and patient size.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Murry T., Carrau R. and Eibling D.. Epidemiology of swallowing disorders In: Comprehensive Management of Swallowing Disorders. Carrau R. and Murry T. Eds. (San Diego: Singular; ) pp. 3–9 (1999).
-
- Howden C. W. Management of acid-related disorders in patients with dysphagia. Am. J. Med. 117(5A), 44S–48S (2004). - PubMed
-
- Domench E. and Kelly J.. Swallowing disorders. Med. Clin. North Am. 83(1), 97–113 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Groher M. E. and Bukatman R.. The prevalence of swallowing disorders in two teaching hospitals. Dysphagia. 1, 3–6 (1986).
-
- Park Y. H., Han H. R., Oh B. M., Lee J., Park J., Yu S. J. and Chang H. K.. Prevalence and associated factors of dysphagia in nursing home residents. Geriatri. Nurs. (New York, NY) 34, 212–217 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

