The effect of delta-like 1 homologue on the proliferation and odontoblastic differentiation in human dental pulp stem cells
- PMID: 28205268
- PMCID: PMC6529117
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12335
The effect of delta-like 1 homologue on the proliferation and odontoblastic differentiation in human dental pulp stem cells
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to investigate the functions of delta-like homologue 1 (DLK1) in the proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs).
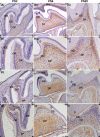
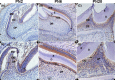
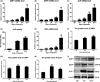
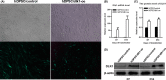
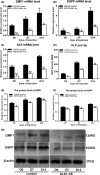
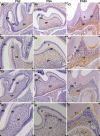
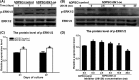
Methods: Immunohistochemical analysis was used to determine the expression of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP), DLK1, NOTCH1 and p-ERK1/2 in the mouse first maxillary molar. Recombinant lentivirus was constructed to overexpress DLK1 stably in hDPSCs. The cell viability and proliferation of hDPSCs were examined by CCK8 and EdU incorporation assay respectively. The odontoblastic differentiation of hDPSCs was determined by detection of ALPase activity assay, ALP and alizarin red staining and the expression of mineralization-related genes including ALP, DSPP and dental matrix protein. The mRNA and protein levels of DLK1 and p-ERK1/2 protein expression were detected. ERK inhibitor was used to test the differentiation effect of DLK1 on hDPSCs.
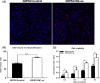
Results: Delta-like homologue 1 was highly expressed on the odontoblasts and dental pulp cells on the first maxillary molar; the expression of p-ERK1/2 is similar with the DLK1 in the same process. The expression level of DLK1 increased significantly after the odontoblastic induction of hDPSCs. DLK1 overexpression increased the proliferation ability of hDPSCs and inhibited odontoblastic differentiation of hDPSCs. The protein level of p-ERK1/2 significantly increased in hDPSCs/dlk1-oe group. ERK signalling pathway inhibitor reversed the odontoblastic differentiation effects of DLK1 on hDPSCs.
Conclusions: The proliferation of hDPSCs was promoted after DLK1 overexpression. DLK1 inhibited the odontoblastic differentiation of hDPSCs, which maybe through ERK signalling pathway.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stathmin inhibits proliferation and differentiation of dental pulp stem cells via sonic hedgehog/Gli.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Jul;22(7):3442-3451. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13621. Epub 2018 Apr 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29655218 Free PMC article.
-
KLF4 promotes the odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp cells.J Endod. 2011 Jul;37(7):948-54. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2011.03.030. Epub 2011 May 13. J Endod. 2011. PMID: 21689550
-
microRNA-143-3p regulates odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through regulation of the osteoprotegerin-RANK ligand pathway by targeting RANK.Exp Physiol. 2020 May;105(5):876-885. doi: 10.1113/EP087992. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Exp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32052500
-
Human dental pulp stem cells and hormesis.Ageing Res Rev. 2022 Jan;73:101540. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101540. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Ageing Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 34890824 Review.
-
Emerging Roles of DLK1 in the Stem Cell Niche and Cancer Stemness.J Histochem Cytochem. 2022 Jan;70(1):17-28. doi: 10.1369/00221554211048951. Epub 2021 Oct 4. J Histochem Cytochem. 2022. PMID: 34606325 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FAM20C could be targeted by TET1 to promote odontoblastic differentiation potential of human dental pulp cells.Cell Prolif. 2018 Apr;51(2):e12426. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12426. Epub 2017 Dec 25. Cell Prolif. 2018. PMID: 29277934 Free PMC article.
-
The odontoblastic differentiation of dental mesenchymal stem cells: molecular regulation mechanism and related genetic syndromes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 25;11:1174579. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1174579. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37818127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of protein delta homolog 1 in the proliferation and differentiation of ameloblasts.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Mar;17(3):3537-3544. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8290. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29257328 Free PMC article.
-
The Genes Involved in Dentinogenesis.Organogenesis. 2022 Dec 31;18(1):1-19. doi: 10.1080/15476278.2021.2022373. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Organogenesis. 2022. PMID: 35023442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sinanan AC, Hunt NP, Lewis MP. Human adult craniofacial muscle‐derived cells: neural‐cell adhesion‐molecule (NCAM; CD56)‐expressing cells appear to contain multipotential stem cells. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2004;40:25–34. - PubMed
-
- Qi SC, Cui C, Yan YH, Sun GH, Zhu SR. Effects of high‐mobility group box 1 on the proliferation and odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp cells. Int Endod J. 2013;46:1153–1163. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

