In vivo dosimetry in UK external beam radiotherapy: current and future usage
- PMID: 28205452
- PMCID: PMC5605079
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20160915
In vivo dosimetry in UK external beam radiotherapy: current and future usage
Abstract
Objective: Towards Safer Radiotherapy recommended that radiotherapy (RT) centres should have protocols in place for in vivo dosimetry (IVD) monitoring at the beginning of patient treatment courses (Donaldson S. Towards safer radiotherapy. R Coll Radiol 2008). This report determines IVD implementation in the UK in 2014, the methods used and makes recommendations on future use.
Methods: Evidence from peer-reviewed journals was used in conjunction with the first survey of UK RT centre IVD practice since the publication of Towards Safer Radiotherapy. In March 2014, profession-specific questionnaires were sent to radiographer, clinical oncologist and physics staff groups in each of the 66 UK RT centres.
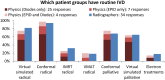
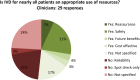
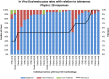
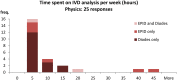
Results: Response rates from each group were 74%, 45% and 74%, respectively. 73% of RT centres indicated that they performed IVD. Diodes are the most popular IVD device. Thermoluminescent dosimeter (TLD) is still in use in a number of centres but not as a sole modality, being used in conjunction with diodes and/or electronic portal imaging device (EPID). The use of EPID dosimetry is increasing and is considered of most potential value for both geometric and dosimetric verification.
Conclusion: Owing to technological advances, such as electronic data transfer, independent monitor unit checking and daily image-guided radiotherapy, the overall risk of adverse treatment events in RT has been substantially reduced. However, the use of IVD may prevent a serious radiation incident. Point dose IVD is not considered suited to the requirements of verifying advanced RT techniques, leaving EPID dosimetry as the current modality likely to be developed as a future standard. Advances in knowledge: An updated perspective on UK IVD use and provision of professional guidelines for future implementation.
Figures









References
-
- Donaldson S. Towards safer radiotherapy. R Coll Radiol 2008.
-
- Implementing in vivo dosimetry. The Royal College of Radiologists, Society and College of Radiographers, Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine, The British Institute of Radiology; 2008.
-
- Donaldson L. On the State of public health: Annual Report of the Chief Medical Officer, Department of Health; 2006.
-
- Vision for Radiotherapy Report. CRUK; 2014. Available from: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/sites/default/files/policy_feb2014_radi....
-
- Fiorino C, Corletto D, Mangili P, Broggi S, Bonini A, Cattaneo GM, et al. . Quality assurance by systematic in vivo dosimetry: results on a large cohort of patients. Radiother Oncol 2000; 56: 85–95. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-8140(00)00195-x - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

