Her2 alterations in muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Patient selection beyond protein expression for targeted therapy
- PMID: 28205537
- PMCID: PMC5311866
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42713
Her2 alterations in muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Patient selection beyond protein expression for targeted therapy
Abstract
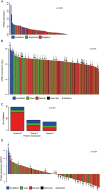
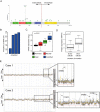
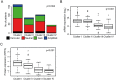
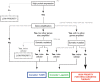
Although the introduction of novel targeted agents has improved patient outcomes in several human cancers, no such advance has been achieved in muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). However, recent sequencing efforts have begun to dissect the complex genomic landscape of MIBC, revealing distinct molecular subtypes and offering hope for implementation of targeted therapies. Her2 (ERBB2) is one of the most established therapeutic targets in breast and gastric cancer but agents targeting Her2 have not yet demonstrated anti-tumor activity in MIBC. Through an integrated analysis of 127 patients from three centers, we identified alterations of Her2 at the DNA, RNA and protein level, and demonstrate that Her2 relevance as a tumor driver likely may vary even within ERBB2 amplified cases. Importantly, tumors with a luminal molecular subtype have a significantly higher rate of Her2 alterations than those of the basal subtype, suggesting that Her2 activity is also associated with subtype status. Although some of our findings present rare events in bladder cancer, our study suggests that comprehensively assessing Her2 status in the context of tumor molecular subtype may help select MIBC patients most likely to respond to Her2 targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Employment: Two authors (C.B., E.D.) are employees of GenomeDx Biosciences, which funded the gene expression analysis of the patient from the NAC cohort and assisted in the bioinformatics data analysis. The remaining authors have no direct or indirect commercial financial incentive associated with publishing the article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunohistochemical based molecular subtypes of muscle-invasive bladder cancer: association with HER2 and EGFR alterations, neoadjuvant chemotherapy response and survival.Diagn Pathol. 2023 Feb 3;18(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13000-023-01295-y. Diagn Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36737799 Free PMC article.
-
ERBB2 Mutations Characterize a Subgroup of Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancers with Excellent Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy.Eur Urol. 2016 Mar;69(3):384-8. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.01.014. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 25636205
-
Nonamplification ERBB2 genomic alterations in 5605 cases of recurrent and metastatic breast cancer: An emerging opportunity for anti-HER2 targeted therapies.Cancer. 2016 Sep 1;122(17):2654-62. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30102. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27284958
-
Using the neoadjuvant chemotherapy paradigm to develop precision therapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Urol Oncol. 2016 Oct;34(10):469-76. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.05.012. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Urol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27317490 Review.
-
Key signaling pathways in the muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma: Clinical markers for disease modeling and optimized treatment.Int J Cancer. 2016 Jun 1;138(11):2562-9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29918. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26547270 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-transcriptional air pollution oxidation to the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway promotes pulmonary stress phenotypes.Commun Biol. 2020 Jul 22;3(1):392. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01118-6. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 32699268 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular subtypes of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder-background and clinical relevance].Urologe A. 2021 Jan;60(1):81-88. doi: 10.1007/s00120-020-01396-2. Urologe A. 2021. PMID: 33242119 Review. German.
-
Response to Anti-HER2-Based Treatment in a Patient with Bladder Adenocarcinoma Harboring HER2 Amplification and S310F Mutation Discovered by Next-Generation Sequencing: A Case Report.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 18;13:4249-4255. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S247515. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32547059 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical based molecular subtypes of muscle-invasive bladder cancer: association with HER2 and EGFR alterations, neoadjuvant chemotherapy response and survival.Diagn Pathol. 2023 Feb 3;18(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13000-023-01295-y. Diagn Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36737799 Free PMC article.
-
A validation and extended description of the Lund taxonomy for urothelial carcinoma using the TCGA cohort.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 27;8(1):3737. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22126-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29487377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Madersbacher S. et al.. Radical cystectomy for bladder cancer today–a homogeneous series without neoadjuvant therapy. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 21, 690–696 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Stein J. P. et al.. Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1,054 patients. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 19, 666–675 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

