microRNA-17 family promotes polycystic kidney disease progression through modulation of mitochondrial metabolism
- PMID: 28205547
- PMCID: PMC5316862
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14395
microRNA-17 family promotes polycystic kidney disease progression through modulation of mitochondrial metabolism
Abstract
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most frequent genetic cause of renal failure. Here we identify miR-17 as a target for the treatment of ADPKD. We report that miR-17 is induced in kidney cysts of mouse and human ADPKD. Genetic deletion of the miR-17∼92 cluster inhibits cyst proliferation and PKD progression in four orthologous, including two long-lived, mouse models of ADPKD. Anti-miR-17 treatment attenuates cyst growth in short-term and long-term PKD mouse models. miR-17 inhibition also suppresses proliferation and cyst growth of primary ADPKD cysts cultures derived from multiple human donors. Mechanistically, c-Myc upregulates miR-17∼92 in cystic kidneys, which in turn aggravates cyst growth by inhibiting oxidative phosphorylation and stimulating proliferation through direct repression of Pparα. Thus, miR-17 family is a promising drug target for ADPKD, and miR-17-mediated inhibition of mitochondrial metabolism represents a potential new mechanism for ADPKD progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Vishal Patel and John Androsavich have applied for a patent related to the treatment of polycystic kidney disease using miR-17 inhibitors. The Patel lab has a sponsored research agreement with Regulus Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
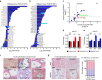
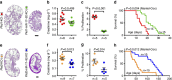

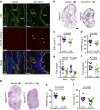





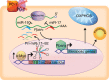
Comment in
-
Polycystic kidney disease: MicroRNA-17: a new drug target for ADPKD.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017 May;13(5):260. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.33. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28262775 No abstract available.
References
-
- Igarashi P. & Somlo S. Polycystic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 18, 1371–1373 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Gabow P. A. & Grantham J. J. in Diseases of the Kidney eds Schrier R. W., Gottschalk C. W. Little, Brown (1997).
-
- Bartel D. P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

