Synergistic chemopreventive effects of nobiletin and atorvastatin on colon carcinogenesis
- PMID: 28207072
- PMCID: PMC6248647
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgx018
Synergistic chemopreventive effects of nobiletin and atorvastatin on colon carcinogenesis
Abstract
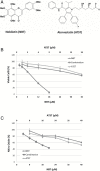
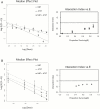
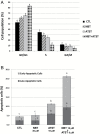
Different cancer chemopreventive agents may act synergistically and their combination may produce enhanced protective effects against carcinogenesis than each individual agent alone. Herein, we investigated the chemopreventive effects of nobiletin (NBT, a citrus polymethoxyflavone) and atorvastatin (ATST, a lipid-lowering drug) in colon cancer cells/macrophages and an azoxymethane (AOM)-induced colon carcinogenesis rat model. The results demonstrated that co-treatments of NBT/ATST produced enhanced growth inhibitory and anti-inflammatory effects on the colon cancer cells and macrophages, respectively. Isobologram analysis confirmed that these interactions between NBT and ATST were synergistic. NBT/ATST co-treatment also synergistically induced extensive cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Oral administration of NBT (0.1%, w/w in diet) or ATST (0.04%, w/w in diet) significantly decreased colonic tumor incidence and multiplicity in AOM-treated rats. Most importantly, co-treatment of NBT/ATST at their half doses (0.05% NBT + 0.02% ATST, w/w in diet) resulted in even stronger inhibitory effects on colonic tumor incidence and multiplicity than did NBT or ATST alone at higher doses. Statistical analysis confirmed that the enhanced chemopreventive activities against colon carcinogenesis in rats by the NBT/ATST combination were highly synergistic. Our results further demonstrated that NBT/ATST co-treatment profoundly modulated key cellular signaling regulators associated with inflammation, cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, apoptosis, angiogenesis and metastasis in the colon of AOM-treated rats. In conclusion, for the first time, our results demonstrated a strong synergy in inhibiting colon carcinogenesis produced by the co-treatment of NBT and ATST, which provided a scientific basis for using NBT in combination with ATST for colon cancer chemoprevention in humans.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Xiao H., et al. (2008) Combination regimen with statins and NSAIDs: a promising strategy for cancer chemoprevention. Int. J. Cancer, 123, 983–990. - PubMed
-
- DiMarco-Crook C., et al. (2015) Diet-based strategies for cancer chemoprevention: the role of combination regimens using dietary bioactive components. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol., 6, 505–526. - PubMed
-
- Bose M., et al. (2007) Inhibition of tumorigenesis in ApcMin/+ mice by a combination of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and fish oil. J. Agric. Food Chem., 55, 7695–7700. - PubMed
-
- Xu G., et al. (2010) Combination of curcumin and green tea catechins prevents dimethylhydrazine-induced colon carcinogenesis. Food Chem. Toxicol., 48, 390–395. - PubMed
-
- Li S.M., et al. (2009) Chemistry and health effects of polymethoxyflavones and hydroxylated polymethoxyflavones. J. Funct. Foods, 1, 2–12.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

