Organ dysfunction during continuous veno-venous high cut-off hemodialysis in patients with septic acute kidney injury: A prospective observational study
- PMID: 28207795
- PMCID: PMC5313216
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172039
Organ dysfunction during continuous veno-venous high cut-off hemodialysis in patients with septic acute kidney injury: A prospective observational study
Abstract
Background: Continuous veno-venous hemodialysis with high cut-off membranes (HCO-CVVHD) removes inflammatory mediators involved in organ dysfunction during sepsis. The aim of the present study was to assess the variations in SOFA score and identify early predictors of short-term mortality in a cohort of patients with septic shock, treated with HCO-CVVHD for acute kidney injury (AKI).
Methods: An observational prospective multicenter cohort study was conducted in four mixed medical-surgical ICUs. Thirty-eight patients with septic shock and AKI (KDIGO stage≥1) treated with HCO-CVVHD have been included in this study. Patients were divided into Survivors and non-Survivors according to mortality observed at 72nd hr of treatment. The variation of SOFA scores and clinical/biochemical parameters were described over time for the entire population and specifically for Survivors and non-Survivors. Similarly, circulating inflammatory mediators (as IL-6, TNF-a and IL-10) were described over time. A logistic regression analysis was used to identify the baseline clinical and biochemical parameters associated with 72 hrs-ICU mortality.
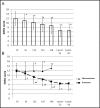
Results: Overall, the mean SOFA score was 12±3 at baseline, 10.9±3 at 6hrs, 9.8±3 at 12hrs, 8.9±3.3 at 24 hrs, and 8±3.5 at 48 hrs after HCO-CVVHD initiation; and 6.5±2.7 at 24 hrs and 6.6±3 at 48 hrs after HCO-CVVHD discontinuation. In the multivariate regression analysis, baseline serum lactate levels and AKI stage independently correlated with short-term mortality during HCO-CVVHD. A significant reduction was observed in circulating levels of TNFα and IL-6 among Survivors.
Conclusions: SOFA score significantly decreased early after initiation of HCO-CVVHD in patients with septic AKI. Baseline lactate levels and the AKI stage resulted to be associated to 72 hrs-ICU-mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of High Cut-Off Hemofilters in the Removal of Selected Cytokines in Patients During Septic Shock Accompanied by Acute Kidney Injury-Preliminary Study.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Nov 13;22:4338-4344. doi: 10.12659/MSM.896819. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27840404 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Markers During Continuous High Cutoff Hemodialysis in Patients with Septic Shock and Acute Kidney Injury.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1251:71-80. doi: 10.1007/5584_2019_458. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31919709
-
Hemodialysis with High Cut-Off Hemodialyzers in Patients with Multi-Drug Resistant Gram-Negative Sepsis and Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective, Case-Control Study.Blood Purif. 2016;42(3):186-93. doi: 10.1159/000446978. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Blood Purif. 2016. PMID: 27352068
-
New insights regarding rationale, therapeutic target and dose of hemofiltration and hybrid therapies in septic acute kidney injury.Blood Purif. 2012;33(1-3):44-51. doi: 10.1159/000333837. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Blood Purif. 2012. PMID: 22179226 Review.
-
[The role of high cut off membranes in renal replacement therapy of acute kidney injury in the course of sepsis - the current state of knowledge].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2018 Sep 21;45(267):99-101. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2018. PMID: 30240377 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Early use of endotoxin absorption by oXiris in abdominal septic shock: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jul 10;99(28):e19632. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019632. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32664051 Free PMC article.
-
Blood purification for sepsis: an overview.Precis Clin Med. 2021 Feb 25;4(1):45-55. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbab005. eCollection 2021 Mar. Precis Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 35693122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: consensus report of the 25th Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) Workgroup.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 Dec;16(12):747-764. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-00356-5. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33060844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clearance of inflammatory cytokines in patients with septic acute kidney injury during renal replacement therapy using the EMiC2 filter (Clic-AKI study).Crit Care. 2021 Jan 28;25(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03476-x. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33509215 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal techniques for the treatment of critically ill patients with sepsis beyond conventional blood purification therapy: the promises and the pitfalls.Crit Care. 2018 Oct 25;22(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2181-z. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30360755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim WY, Huh JW, Lim C-M, Koh Y, Hong S-B. Analysis of progression in risk, injury, failure, loss, and end-stage renal disease classification on outcome in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. J Crit Care. 2012;27: 104.e1–7. - PubMed
-
- Honore PM, Jacobs R, Joannes-Boyau O, De Regt J, Boer W, De Waele E, et al. Septic AKI in ICU patients. diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment type, dosing, and timing: a comprehensive review of recent and future developments. Ann Intensive Care. Springer Open Ltd; 2011;1: 32 10.1186/2110-5820-1-32 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angus DCD, van der Poll T. Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. N Eng J Med. 2013;369: 840–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

