JMJD-5/KDM8 regulates H3K36me2 and is required for late steps of homologous recombination and genome integrity
- PMID: 28207814
- PMCID: PMC5336306
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006632
JMJD-5/KDM8 regulates H3K36me2 and is required for late steps of homologous recombination and genome integrity
Abstract
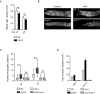
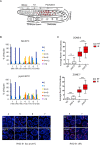
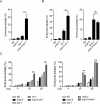
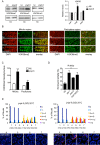
The eukaryotic genome is organized in a three-dimensional structure called chromatin, constituted by DNA and associated proteins, the majority of which are histones. Post-translational modifications of histone proteins greatly influence chromatin structure and regulate many DNA-based biological processes. Methylation of lysine 36 of histone 3 (H3K36) is a post-translational modification functionally relevant during early steps of DNA damage repair. Here, we show that the JMJD-5 regulates H3K36 di-methylation and it is required at late stages of double strand break repair mediated by homologous recombination. Loss of jmjd-5 results in hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation and in meiotic defects, and it is associated with aberrant retention of RAD-51 at sites of double strand breaks. Analyses of jmjd-5 genetic interactions with genes required for resolving recombination intermediates (rtel-1) or promoting the resolution of RAD-51 double stranded DNA filaments (rfs-1 and helq-1) suggest that jmjd-5 prevents the formation of stalled postsynaptic recombination intermediates and favors RAD-51 removal. As these phenotypes are all recapitulated by a catalytically inactive jmjd-5 mutant, we propose a novel role for H3K36me2 regulation during late steps of homologous recombination critical to preserve genome integrity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

