TMG-123, a novel glucokinase activator, exerts durable effects on hyperglycemia without increasing triglyceride in diabetic animal models
- PMID: 28207836
- PMCID: PMC5313197
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172252
TMG-123, a novel glucokinase activator, exerts durable effects on hyperglycemia without increasing triglyceride in diabetic animal models
Abstract
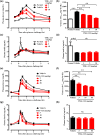
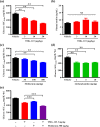
Glucokinase (GK) plays a critical role for maintaining glucose homeostasis with regulating glucose uptake in liver and insulin secretion in pancreas. GK activators have been reported to decrease blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, clinical development of GK activators has failed due to the loss of glucose-lowering effects and increased plasma triglyceride levels after chronic treatment. Here, we generated a novel GK activator, TMG-123, examined its in vitro and in vivo pharmacological characteristics, and evaluated its risks of aforementioned clinical issues. TMG-123 selectively activated GK enzyme activity without increasing Vmax. TMG-123 improved glucose tolerance without increasing plasma insulin levels in both insulin-deficient (Goto-Kakizaki rats) and insulin-resistant (db/db mice) models. The beneficial effect on glucose tolerance was greater than results observed with clinically available antidiabetic drugs such as metformin and glibenclamide in Zucker Diabetic Fatty rats. TMG-123 also improved glucose tolerance in combination with metformin. After 4 weeks of administration, TMG-123 reduced the Hemoglobin A1c levels without affecting liver and plasma triglyceride levels in Goto-Kakizaki rats and Diet-Induced Obesity mice. Moreover, TMG-123 sustained its effect on Hemoglobin A1c levels even after 24 weeks of administration without affecting triglycerides. Taken together, these data indicate that TMG-123 exerts glucose-lowering effects in both insulin-deficient and -resistant diabetes, and sustains reduced Hemoglobin A1c levels without affecting hepatic and plasma triglycerides even after chronic treatment. Therefore, TMG-123 is expected to be an antidiabetic drug that overcomes the concerns previously reported with other GK activators.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chronic glucokinase activator treatment at clinically translatable exposures gives durable glucose lowering in two animal models of type 2 diabetes.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Apr;171(7):1642-54. doi: 10.1111/bph.12504. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24772484 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic glucokinase activation reduces glycaemia and improves glucose tolerance in high-fat diet fed mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Aug 1;663(1-3):80-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.05.009. Epub 2011 May 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21586282
-
Allosteric activators of glucokinase: potential role in diabetes therapy.Science. 2003 Jul 18;301(5631):370-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1084073. Science. 2003. PMID: 12869762
-
Two birds with one stone: novel glucokinase activator stimulates glucose-induced pancreatic insulin secretion and augments hepatic glucose metabolism.Mol Interv. 2003 Oct;3(7):367-70. doi: 10.1124/mi.3.7.367. Mol Interv. 2003. PMID: 14993457 Review.
-
Small molecule glucokinase activators as novel anti-diabetic agents.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Apr;33(Pt 2):371-4. doi: 10.1042/BST0330371. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 15787609 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural products, an important resource for discovery of multitarget drugs and functional food for regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Jan 10;12:121-135. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S151860. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 29391777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral metabolic effects of ozone exposure in healthy and diabetic rats on normal or high-cholesterol diet.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 15;415:115427. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115427. Epub 2021 Jan 30. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33524448 Free PMC article.
-
Anthocyanins from purple corn activate free fatty acid-receptor 1 and glucokinase enhancing in vitro insulin secretion and hepatic glucose uptake.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 11;13(7):e0200449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200449. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29995924 Free PMC article.
-
Implications for Drug Characterization in Glucose Tolerance Tests Without Insulin: Simulation Study of Power and Predictions Using Model-Based Analysis.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;6(10):686-694. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12214. Epub 2017 Sep 25. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28575547 Free PMC article.
-
A Recent Achievement In the Discovery and Development of Novel Targets for the Treatment of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Exp Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 10;12:1-15. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S226113. eCollection 2020. J Exp Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32021494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37 Suppl 1: S81–90. - PubMed
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38(1): 140–149. 10.2337/dc14-2441 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilson JE. Hexokinases. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1995; 126: 65–198. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

