Non-small cell lung cancer: Whole-lesion histogram analysis of the apparent diffusion coefficient for assessment of tumor grade, lymphovascular invasion and pleural invasion
- PMID: 28207858
- PMCID: PMC5313135
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172433
Non-small cell lung cancer: Whole-lesion histogram analysis of the apparent diffusion coefficient for assessment of tumor grade, lymphovascular invasion and pleural invasion
Abstract
Purpose: Investigating the diagnostic accuracy of histogram analyses of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values for determining non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumor grades, lymphovascular invasion, and pleural invasion.
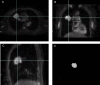
Materials and methods: We studied 60 surgically diagnosed NSCLC patients. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) was performed in the axial plane using a navigator-triggered single-shot, echo-planar imaging sequence with prospective acquisition correction. The ADC maps were generated, and we placed a volume-of-interest on the tumor to construct the whole-lesion histogram. Using the histogram, we calculated the mean, 5th, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, and 95th percentiles of ADC, skewness, and kurtosis. Histogram parameters were correlated with tumor grade, lymphovascular invasion, and pleural invasion. We performed a receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis to assess the diagnostic performance of histogram parameters for distinguishing different pathologic features.
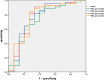
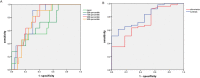
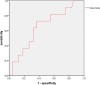
Results: The ADC mean, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, and 95th percentiles showed significant differences among the tumor grades. The ADC mean, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, and 95th percentiles were significant histogram parameters between high- and low-grade tumors. The ROC analysis between high- and low-grade tumors showed that the 95th percentile ADC achieved the highest area under curve (AUC) at 0.74. Lymphovascular invasion was associated with the ADC mean, 50th, 75th, 90th, and 95th percentiles, skewness, and kurtosis. Kurtosis achieved the highest AUC at 0.809. Pleural invasion was only associated with skewness, with the AUC of 0.648.
Conclusions: ADC histogram analyses on the basis of the entire tumor volume are able to stratify NSCLCs' tumor grade, lymphovascular invasion and pleural invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient map of diffusion-weighted MRI in endometrial cancer: a preliminary correlation study with histological grade.Acta Radiol. 2014 Dec;55(10):1270-7. doi: 10.1177/0284185113514967. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Acta Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24316663
-
Preoperative histogram analysis of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) for predicting microvascular invasion in patients with single hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Radiol. 2018 Aug;105:65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.05.032. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Eur J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30017300
-
Correlation of histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient with uterine cervical pathologic finding.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015 May;204(5):1125-31. doi: 10.2214/AJR.14.13350. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015. PMID: 25905952
-
Application of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Histogram Metrics for Differentiation of Pediatric Posterior Fossa Tumors : A Large Retrospective Study and Brief Review of Literature.Clin Neuroradiol. 2022 Dec;32(4):1097-1108. doi: 10.1007/s00062-022-01179-6. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Clin Neuroradiol. 2022. PMID: 35674799 Review.
-
Diagnostic performance of whole-lesion apparent diffusion coefficient histogram analysis metrics for differentiating benign and malignant breast lesions: a systematic review and diagnostic meta-analysis.Acta Radiol. 2020 Sep;61(9):1165-1175. doi: 10.1177/0284185119896520. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Acta Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31924104
Cited by
-
Volumetric ADC histogram analysis for preoperative evaluation of LVSI status in stage I endometrioid adenocarcinoma.Eur Radiol. 2022 Jan;32(1):460-469. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07996-6. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34137929
-
Effectiveness of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values in Predicting Pathologic Subtypes and Grade in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 16;14(16):1795. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14161795. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202283 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of chemotherapy resistance changes in human colorectal cancer xenografts in rats based on MRI histogram features.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 31;14:1301649. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1301649. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38357206 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-volume ADC histogram of the brain as an image biomarker in evaluating disease severity of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.Front Neurol. 2022 Aug 3;13:918554. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.918554. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35989925 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of brain metastases originating from lung and breast cancers using apparent diffusion coefficient histogram analysis and the relation of histogram parameters with Ki-67.Neuroradiol J. 2022 Jun;35(3):370-377. doi: 10.1177/19714009211049082. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Neuroradiol J. 2022. PMID: 34609916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Higashi K, Ito K, Hiramatsu Y, Ishikawa T, Sakuma T, Matsunari I, et al. 18F-FDG uptake by primary tumors as a predictor of intratumoral lymphatic vessel invasion and lymph node involvement in non-small cell lung cancer: analysis of a multi-center study. J Nucl Med 2005;46(2):267–273. - PubMed
-
- Guo JF, Higashi K, Ueda Y, Ishigaki Y, Sakuma T, Oguchi M, et al. VEGF-A and its isoform VEGF121 mRNA expression measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR: correlation with F-18 FDG uptake and aggressiveness of lung adenocarcinoma: preliminary study. Ann Nucl Med 2011;25(1):29–36. 10.1007/s12149-010-0427-1 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

