Distinct susceptibility and applicability of MDCK derivatives for influenza virus research
- PMID: 28207898
- PMCID: PMC5313193
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172299
Distinct susceptibility and applicability of MDCK derivatives for influenza virus research
Abstract
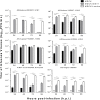
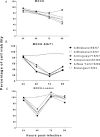
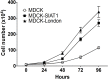
Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells are widely utilized as a substrate for influenza virus isolation and propagation due to the high yields of virus. Here we compared the conventional MDCK cell line, MDCK-SIAT1 and MDCK-London for viral production, cell survival, and suitability in testing antivirals using six influenza strains including two H1N1 (pandemic and epidemic strains), three H3N2 and one influenza B strain. Overall our results suggest that MDCK-London cell line is superior for virus culturing and quantification, and hence an ideal platform to evaluate antiviral drug efficacy against multiple strains of influenza. Our data also suggests that while virus titers determined by the hemagglutination assay (HA) and neuraminidase activity (NA) are widely used to indicate viral load, there is a poor correlation between these measurements and the infectious titer obtained by plaque assay.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hussain AI, Cordeiro M, Sevilla E, Liu J. Comparison of egg and high yielding MDCK cell-derived live attenuated influenza virus for commercial production of trivalent influenza vaccine: in vitro cell susceptibility and influenza virus replication kinetics in permissive and semi-permissive cells. Vaccine. 2010;28(22):3848–55. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.03.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schepetiuk SK, Kok T. The use of MDCK, MEK and LLC-MK2 cell lines with enzyme immunoassay for the isolation of influenza and parainfluenza viruses from clinical specimens. J Virol Methods. 1993;42(2–3):241–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

