Industry sponsorship and research outcome
- PMID: 28207928
- PMCID: PMC8132492
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.MR000033.pub3
Industry sponsorship and research outcome
Abstract
Background: Clinical research affecting how doctors practice medicine is increasingly sponsored by companies that make drugs and medical devices. Previous systematic reviews have found that pharmaceutical-industry sponsored studies are more often favorable to the sponsor's product compared with studies with other sources of sponsorship. A similar association between sponsorship and outcomes have been found for device studies, but the body of evidence is not as strong as for sponsorship of drug studies. This review is an update of a previous Cochrane review and includes empirical studies on the association between sponsorship and research outcome.
Objectives: To investigate whether industry sponsored drug and device studies have more favorable outcomes and differ in risk of bias, compared with studies having other sources of sponsorship.
Search methods: In this update we searched MEDLINE (2010 to February 2015), Embase (2010 to February 2015), the Cochrane Methodology Register (2015, Issue 2) and Web of Science (June 2015). In addition, we searched reference lists of included papers, previous systematic reviews and author files.
Selection criteria: Cross-sectional studies, cohort studies, systematic reviews and meta-analyses that quantitatively compared primary research studies of drugs or medical devices sponsored by industry with studies with other sources of sponsorship. We had no language restrictions.
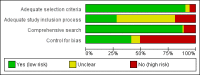
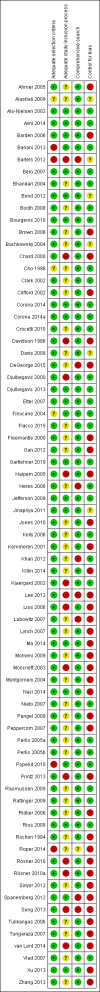
Data collection and analysis: Two assessors screened abstracts and identified and included relevant papers. Two assessors extracted data, and we contacted authors of included papers for additional unpublished data. Outcomes included favorable results, favorable conclusions, effect size, risk of bias and whether the conclusions agreed with the study results. Two assessors assessed risk of bias of included papers. We calculated pooled risk ratios (RR) for dichotomous data (with 95% confidence intervals (CIs)).
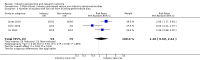
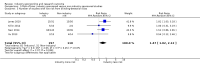
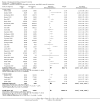
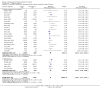
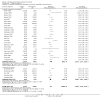
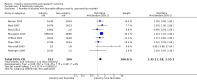
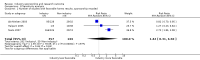
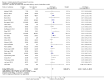
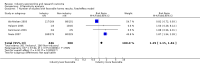
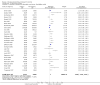
Main results: Twenty-seven new papers were included in this update and in total the review contains 75 included papers. Industry sponsored studies more often had favorable efficacy results, RR: 1.27 (95% CI: 1.17 to 1.37) (25 papers) (moderate quality evidence), similar harms results RR: 1.37 (95% CI: 0.64 to 2.93) (four papers) (very low quality evidence) and more often favorable conclusions RR: 1.34 (95% CI: 1.19 to 1.51) (29 papers) (low quality evidence) compared with non-industry sponsored studies. Nineteen papers reported on sponsorship and efficacy effect size, but could not be pooled due to differences in their reporting of data and the results were heterogeneous. We did not find a difference between drug and device studies in the association between sponsorship and conclusions (test for interaction, P = 0.98) (four papers). Comparing industry and non-industry sponsored studies, we did not find a difference in risk of bias from sequence generation, allocation concealment, follow-up and selective outcome reporting. However, industry sponsored studies more often had low risk of bias from blinding, RR: 1.25 (95% CI: 1.05 to 1.50) (13 papers), compared with non-industry sponsored studies. In industry sponsored studies, there was less agreement between the results and the conclusions than in non-industry sponsored studies, RR: 0.83 (95% CI: 0.70 to 0.98) (six papers).
Authors' conclusions: Sponsorship of drug and device studies by the manufacturing company leads to more favorable efficacy results and conclusions than sponsorship by other sources. Our analyses suggest the existence of an industry bias that cannot be explained by standard 'Risk of bias' assessments.
Conflict of interest statement
Andreas Lundh, Joel Lexchin and Lisa Bero are authors of the some of the previous reviews and included studies.
In 2015 to 2016, Joel Lexchin received payment from non‐profit entities for being a consultant on two projects, one looking at indications‐based prescribing and a second looking at which drugs should be provided free of charge by general practitioners. He received payment from a for‐profit company for being on a panel that discussed expanding drug coverage in Canada. He is on the Foundation Board of Health Action International.
In 2014, Barbara Mintzes was retained as an expert witness by the law firm representing the plaintiffs in a Canadian class action on hormone replacement therapy and breast cancer, and in 2015 to 2016 in an application for a Canadian class action on cardiovascular risks of testosterone supplements. She was a member of the Health Action International – Europe Association Board from 2012 to 2015.
The review authors have no other relevant interests.
Figures























Update of
-
Industry sponsorship and research outcome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12:MR000033. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000033.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 16;2:MR000033. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000033.pub3. PMID: 23235689 Updated.
Comment in
-
Cochrane in CORR ®: Industry Sponsorship and Research Outcome.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Sep;475(9):2159-2164. doi: 10.1007/s11999-017-5421-7. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 28634896 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Ahmer 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ahmer S, Arya P, Anderson D, Faruqui R. Conflict of interest in psychiatry. Psychiatrist 2005;29(8):302‐4.
Alasbali 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Alasbali T, Smith M, Geffen N, Trope GE, Flanagan JG, Jin Y, et al. Discrepancy between results and abstract conclusions in industry‐ vs nonindustry‐funded studies comparing topical prostaglandins. American Journal of Ophthalmology 2009;147(1):33‐8.e2. - PubMed
Als‐Nielsen 2003 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Als‐Nielsen B, Chen W, Gluud C, Kjaergard LL. Association of funding and conclusions in randomized drug trials: a reflection of treatment effect or adverse events?. JAMA 2003;290(7):921‐8. - PubMed
Avni 2014 {published data only}
-
- Avni T, Shiber‐Ofer S, Leibovici L, Paul M. Assessment of bias in outcomes reported in trials on pneumonia: a systematic review. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 2014;33(6):969‐74. - PubMed
Barden 2006 {published data only}
-
- Barden J, Derry S, McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Bias from industry trial funding? A framework, a suggested approach, and a negative result. Pain 2006;121(3):207‐18. - PubMed
Bariani 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bariani GM, Celis Ferrari AC, Hoff PM, Krzyzanowska MK, Riechelmann RP. Self‐reported conflicts of interest of authors, trial sponsorship, and the interpretation of editorials and related phase III trials in oncology. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2013;31(18):2289‐95. - PubMed
Bartels 2012 {published data only}
Bero 2007 {published and unpublished data}
Bhandari 2004 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Bond 2012 {published and unpublished data}
Booth 2008 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Bourgeois 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bourgeois FT, Murthy S, Mandl KD. Outcome reporting among drug trials registered in ClinicalTrials.gov. Annals of Internal Medicine 2010;153(3):158‐66. - PMC - PubMed
Brown 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Brown A, Kraft D, Schmitz SM, Sharpless V, Martin C, Shah R, et al. Association of industry sponsorship to published outcomes in gastrointestinal clinical research. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2006;4(12):1445‐51. - PubMed
Buchkowsky 2004 {published data only}
-
- Buchkowsky SS, Jewesson PJ. Industry sponsorship and authorship of clinical trials over 20 years. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2004;38(4):579‐85. - PubMed
Chard 2000 {published and unpublished data}
Cho 1996 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Cho MK, Bero LA. The quality of drug studies published in symposium proceedings. Annals of Internal Medicine 1996;124(5):485‐9. - PubMed
Clark 2002 {published and unpublished data}
Clifford 2002 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Corona 2014 {published data only}
-
- Corona G, Maseroli E, Rastrelli G, Isidori AM, Sforza A, Mannucci E, et al. Cardiovascular risk associated with testosterone‐boosting medications: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Expert Opinion on Drug Safety 2014;13(10):1327‐51. - PubMed
Corona 2014a {published data only}
-
- Corona G, Isidori AM, Buvat J, Aversa A, Rastrelli G, Hackett G, et al. Testosterone supplementation and sexual function: a meta‐analysis study. Journal of Sexual Medicine 2014;11(6):1577‐92. - PubMed
Crocetti 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Crocetti MT, Amin DD, Scherer R. Assessment of risk of bias among pediatric randomized controlled trials. Pediatrics 2010;126(2):298‐305. - PubMed
Davidson 1986 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Davidson RA. Source of funding and outcome of clinical trials. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1986;1(3):155‐8. - PubMed
Davis 2008 {published data only}
-
- Davis JM, Chen N, Glick ID. Issues that may determine the outcome of antipsychotic trials: industry sponsorship and extrapyramidal side effect. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008;33(5):971‐5. - PubMed
DeGeorge 2015 {published data only}
-
- DeGeorge BR Jr, Holland MC, Drake DB. The impact of conflict of interest in abdominal wall reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix. Annals of Plastic Surgery 2015;74(2):242‐7. - PubMed
Djulbegovic 2000 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Djulbegovic B, Lacevic M, Cantor A, Fields KK, Bennett CL, Adams JR, et al. The uncertainty principle and industry‐sponsored research. Lancet 2000;356(9230):635‐8. - PubMed
Djulbegovic 2013 {published and unpublished data}
Etter 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Etter JF, Burri M, Stapleton J. The impact of pharmaceutical company funding on results of randomized trials of nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation: a meta‐analysis. Addiction 2007;102(5):815‐22. - PubMed
Finucane 2004 {published data only}
-
- Finucane TE, Boult CE. Association of funding and findings of pharmaceutical research at a meeting of a medical professional society. American Journal of Medicine 2004;117(11):842‐5. - PubMed
Flacco 2015 {published data only}
-
- Flacco ME, Manzoli L, Boccia S, Capasso L, Aleksovska K, Rosso A, et al. Head‐to‐head randomized trials are mostly industry sponsored and almost always favor the industry sponsor. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2015;68(7):811‐20. - PubMed
Freemantle 2000 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Freemantle N, Anderson IM, Young P. Predictive value of pharmacological activity for the relative efficacy of antidepressant drugs. Meta‐regression analysis. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;177:292‐302. - PubMed
Gan 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gan HK, You B, Pond GR, Chen EX. Assumptions of expected benefits in randomized phase III trials evaluating systemic treatments for cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2012;104(8):590‐8. - PubMed
Gartlehner 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gartlehner G, Morgan L, Thieda P, Fleg A. The effect of study sponsorship on a systematically evaluated body of evidence of head‐to‐head trials was modest: secondary analysis of a systematic review. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2010;63(2):117‐25. - PubMed
Halpern 2005 {published data only}
-
- Halpern SD, Barton TD, Gross R, Hennessy S, Berlin JA, Strom BL. Epidemiologic studies of adverse effects of anti‐retroviral drugs: how well is statistical power reported. Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety 2005;14(3):155‐61. - PubMed
Heres 2006 {published data only}
-
- Heres S, Davis J, Maino K, Jetzinger E, Kissling W, Leucht S. Why olanzapine beats risperidone, risperidone beats quetiapine, and quetiapine beats olanzapine: An exploratory analysis of head‐to‐head comparison studies of second‐generation antipsychotics. American Journal of Psychiatry 2006;163(2):185‐94. - PubMed
Jefferson 2009 {published and unpublished data}
Jinapriya 2011 {published data only}
-
- Jinapriya D, Anraku A, Alasbali T, Trope GE, Buys YM. Evaluation of investigator bias in industry‐funded clinical trials of latanoprost. Canadian Journal of Ophthalmology 2011;46(6):531‐6. - PubMed
Jones 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jones R, Younie S, Macallister A, Thornton J. A comparison of the scientific quality of publicly and privately funded randomized controlled drug trials. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice 2010;16(6):1322‐5. - PubMed
Kelly 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kelly RE Jr, Cohen LJ, Semple RJ, Bialer P, Lau A, Bodenheimer A, et al. Relationship between drug company funding and outcomes of clinical psychiatric research. Psychological Medicine 2006;36(11):1647‐56. - PubMed
Kemmeren 2001 {published data only}
Khan 2012 {published data only}
Killin 2014 {published data only}
Kjaergard 2002 {published and unpublished data}
Lee 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Lee YK, Chung CY, Koo KH, Lee KM, Ji HM, Park MS. Conflict of interest in the assessment of thromboprophylaxis after total joint arthroplasty: a systematic review. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American volume 2012;94(1):27‐33. - PubMed
Liss 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Liss H. Publication bias in the pulmonary/allergy literature: effect of pharmaceutical company sponsorship. Israel Medical Association Journal 2006;8(7):451‐4. - PubMed
Lubowitz 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lubowitz JH, Appleby D, Centeno JM, Woolf SK, Reid JB 3rd. The relationship between the outcome of studies of autologous chondrocyte implantation and the presence of commercial funding. American Journal of Sports Medicine 2007;35(11):1809‐16. - PubMed
Lynch 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lynch JR, Cunningham MR, Warme WJ, Schaad DC, Wolf FM, Leopold SS. Commercially funded and United States‐based research is more likely to be published; good‐quality studies with negative outcomes are not. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American volume 2007;89(5):1010‐8. - PubMed
Ma 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ma D, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Li L. Comparative efficacy, acceptability, and safety of medicinal, cognitive‐behavioral therapy, and placebo treatments for acute major depressive disorder in children and adolescents: a multiple‐treatments meta‐analysis. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2014;30(6):971‐95. - PubMed
Momeni 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Momeni A, Becker A, Bannasch H, Antes G, Blümle A, Stark GB. Association between research sponsorship and study outcome in plastic surgery literature. Annals of Plastic Surgery 2009;63(6):661‐4. - PubMed
Moncrieff 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Moncrieff J. Clozapine v. conventional antipsychotic drugs for treatment‐resistant schizophrenia: A re‐examination. British Journal of Psychiatry 2003;183:161‐6. - PubMed
Montgomery 2004 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Montgomery JH, Byerly M, Carmody T, Li B, Miller DR, Varghese F, et al. An analysis of the effect of funding source in randomized clinical trials of second generation antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia. Controlled Clinical Trials 2004;25(6):598‐612. - PubMed
Naci 2014 {published and unpublished data}
Nieto 2007 {published data only}
-
- Nieto A, Mazon A, Pamies R, Linana JJ, Lanuza A, Jiménez FO, et al. Adverse effects of inhaled corticosteroids in funded and nonfunded studies. Archives of Internal Medicine 2007;167(19):2047‐53. - PubMed
Pengel 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pengel LH, Barcena L, Morris PJ. The quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials in solid organ transplantation. Transplant International 2009;22(4):377‐84. - PubMed
Peppercorn 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Peppercorn J, Blood E, Winer E, Partridge A. Association between pharmaceutical involvement and outcomes in breast cancer clinical trials. Cancer 2007;109(7):1239‐46. - PubMed
Perlis 2005a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Perlis CS, Harwood M, Perlis RH. Extent and impact of industry sponsorship conflicts of interest in dermatology research. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;52(6):967‐71. - PubMed
Perlis 2005b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Perlis RH, Perlis CS, Wu Y, Hwang C, Joseph M, Nierenberg AA. Industry sponsorship and financial conflict of interest in the reporting of clinical trials in psychiatry. American Journal of Psychiatry 2005;162(10):1957‐60. - PubMed
Popelut 2010 {published and unpublished data}
Printz 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Printz JO, Lee JJ, Knesek M, Urquhart AG. Conflict of interest in the assessment of hyaluronic acid injections for osteoarthritis of the knee: an updated systematic review. Journal of Arthroplasty 2013;28(8 Suppl):30‐33.e1. - PubMed
Rasmussen 2009 {published and unpublished data}
Rattinger 2009 {published and unpublished data}
Ridker 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ridker PM, Torres J. Reported outcomes in major cardiovascular clinical trials funded by for‐profit and not‐for‐profit organizations: 2000‐2005. JAMA 2006;295(19):2270‐4. - PubMed
Rios 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Rios LP, Odueyungbo A, Moitri MO, Rahman MO, Thabane L. Quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials in general endocrinology literature. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2008;93(10):3810‐6. - PubMed
Rochon 1994 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Rochon PA, Gurwitz JH, Simms RW, Fortin PR, Felson DT, Minaker KL, et al. A study of manufacturer‐supported trials of nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs in the treatment of arthritis. Archives of Internal Medicine 1994;154(2):157‐63. - PubMed
Roper 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Roper N, Zhang N, Korenstein D. Industry collaboration and randomized clinical trial design and outcomes. JAMA Internal Medicine 2014;174(10):1695‐6. - PubMed
Rösner 2010 {published data only}
Rösner 2010a {published data only}
Sinyor 2012 {published data only}
-
- Sinyor M, Schaffer A, Smart KA, Levitt AJ, Lanctot KL, Grysman NH. Sponsorship, antidepressant dose, and outcome in major depressive disorder: meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2012;73(2):e277‐87. - PubMed
Spanemberg 2012 {published data only}
-
- Spanemberg L, Massuda R, Lovato L, Paim L, Vares EA, Sica da Rocha N, et al. Pharmacological treatment of bipolar depression: qualitative systematic review of double‐blind randomized clinical trials. Psychiatric Quarterly 2012;83(2):161‐75. - PubMed
Sung 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sung KH, Chung CY, Lee KM, Lee YK, Lee SY, Lee J, et al. Conflict of interest in the assessment of botulinum toxin A injections in patients with cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics 2013;33(5):494‐500. - PubMed
Tulikangas 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tulikangas PK, Ayers A, O'Sullivan DM. A meta‐analysis comparing trials of antimuscarinic medications funded by industry or not. BJU International 2006;98(2):377‐80. - PubMed
Tungaraza 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Tungaraza T, Poole R. Influence of drug company authorship and sponsorship on drug trial outcomes. British Journal of Psychiatry 2007;191:82‐3. - PubMed
van Lent 2014 {published data only}
Vlad 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Vlad SC, LaValley MP, McAlindon TE, Felson DT. Glucosamine for pain in osteoarthritis: why do trial results differ?. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2007;56(7):2267‐77. - PubMed
Xu 2013 {published data only}
Zhang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zhang JP, Gallego JA, Robinson DG, Malhotra AK, Kane JM, Correll CU. Efficacy and safety of individual second‐generation vs. first‐generation antipsychotics in first‐episode psychosis: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2013;16(6):1205‐18. - PMC - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Adams 2013 {published data only}
Adams 2014 {published data only}
Afshari 2011 {published data only}
-
- Afshari A. Evidence based evaluation of immuno‐coagulatory interventions in critical care. Danish Medical Bulletin 2011;58(9):B4316. - PubMed
Alves 2013 {published data only}
-
- Alves M, Fonseca EC, Alves MF, Malki LT, Arruda GV, Reinach PS, et al. Dry eye disease treatment: a systematic review of published trials and a critical appraisal of therapeutic strategies. Ocular Surface 2013;11(3):181‐92. - PubMed
Amiri 2014 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Amiri AR, Kanesalingam K, Cro S, Casey AT. Does source of funding and conflict of interest influence the outcome and quality of spinal research?. Spine Journal 2014;14(2):308‐14. - PubMed
Aneja 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Aneja A, Esquitin R, Shah K, Iyengar R, Nisenbaum R, Melo M, et al. Authors' self‐declared financial conflicts of interest do not impact the results of major cardiovascular trials. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2013;61(11):1137‐43. - PubMed
Apler 2011 {published data only}
Auerbach 2013 {published data only}
-
- Auerbach JD, McGowan KB, Halevi M, Gerling MC, Sharan AD, Whang PG, et al. Mitigating adverse event reporting bias in spine surgery. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American volume 2013;95(16):1450‐6. - PubMed
Baethge 2013 {published data only}
-
- Baethge C, Assall OP, Baldessarini RJ. Systematic review of blinding assessment in randomized controlled trials in schizophrenia and affective disorders 2000‐2010. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics 2013;82(3):152‐60. - PubMed
Bailey 2011 {published data only}
Baker 2013 {published data only}
-
- Baker JR, Vandal AC, Yeoh J, Zeng I, Wong S, Ryan SN. Clinical trial participation improves outcome: a matched historical cohort study. Clinical Trials 2013;10(5):735‐43. - PubMed
Bala 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bala MM, Akl EA, Sun X, Bassler D, Mertz D, Mejza F, et al. Randomized trials published in higher vs. lower impact journals differ in design, conduct, and analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(3):286‐95. - PubMed
Balevi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Balevi B. Industry sponsored research may report more favourable outcomes. Evidence‐Based Dentistry 2011;12(1):5‐6. - PubMed
Barbui 2011 {published data only}
Batalla 2011 {published data only}
-
- Batalla A, Garcia‐Doval I, Aranegui B, Garcia‐Cruz A. Who funds research by Spanish dermatologists? Comparative analysis of articles published in 2008 [¿Quien financia la investigacion de los dermatologos espanoles? Analisis del ano 2008 y comparacion con otros grupos.]. Actas Dermo‐Sifiliograficas 2011;102(7):517‐26. - PubMed
Bennett 2010 {published data only}
Bourgeois 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bourgeois FT, Murthy S, Mandl KD. Comparative effectiveness research: an empirical study of trials registered in ClinicalTrials.gov. PLoS One 2012;7(1):e28820. - PMC - PubMed
Brignardello‐Petersen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Brignardello‐Petersen R, Carrasco‐Labra A, Yanine N, Ulloa C, Araya I, Pintor F, et al. Positive association between conflicts of interest and reporting of positive results in randomized clinical trials in dentistry. Journal of the American Dental Association 2013;144(10):1165‐70. - PubMed
Buesching 2012 {published data only}
-
- Buesching DP, Luce BR, Berger ML. The role of private industry in pragmatic comparative effectiveness trials. Journal of Comparative Effectiveness Research 2012;1(2):147‐56. - PubMed
Califf 2012 {published data only}
-
- Califf RM, Zarin DA, Kramer JM, Sherman RE, Aberle LH, Tasneem A. Characteristics of clinical trials registered in ClinicalTrials.gov, 2007‐2010. JAMA 2012;307(17):1838‐47. - PubMed
Catala‐Lopez 2013 {published data only}
Chaturvedi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Chaturvedi S, Lipszyc DH, Licht C, Craig JC, Parekh R. Pharmacological interventions for hypertension in children. Evidence‐Based Child Health : a Cochrane Review Journal 2014;9(3):498‐580. - PubMed
Chen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Chen Z, Ba G, Shen T, Fu Q. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein‐2 versus autogenous iliac crest bone graft for lumbar fusion: a meta‐analysis of ten randomized controlled trials. Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery 2012;132(12):1725‐40. - PubMed
Chowers 2009 {published data only}
-
- Chowers MY, Gottesman BS, Leibovici L, Pielmeier U, Andreassen S, Paul M. Reporting of adverse events in randomized controlled trials of highly active antiretroviral therapy: systematic review. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2009;64(2):239‐50. - PubMed
Cipriani 2012 {published data only}
Cipriani 2012a {published data only}
Conen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Conen D, Torres J, Ridker PM. Differential citation rates of major cardiovascular clinical trials according to source of funding a survey from 2000 to 2005. Circulation 2008;118(13):1321‐7. - PubMed
Cordoba 2010 {published data only}
Cosgrove 2011 {published data only}
Cunningham 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Cunningham MR, Warme WJ, Schaad DC, Wolf FM, Leopold SS. Industry‐funded positive studies not associated with better design or larger size. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 2007;457:235‐41. - PubMed
Deb 2014 {published data only}
-
- Deb S, Farmah BK, Arshad E, Deb T, Roy M, Unwin GL. The effectiveness of aripiprazole in the management of problem behaviour in people with intellectual disabilities, developmental disabilities and/or autistic spectrum disorder‐‐a systematic review. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2014;35(3):711‐25. - PubMed
Demicheli 2014 {published data only}
Do 2015 {published data only}
Dufka 2014 {published data only}
Dunn 2012 {published data only}
-
- Dunn AG, Gallego B, Coiera E. Industry influenced evidence production in collaborative research communities: a network analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2012;65(5):535‐43. - PubMed
Dunn 2014 {published data only}
-
- Dunn AG, Arachi D, Hudgins J, Tsafnat G, Coiera E, Bourgeois FT. Financial conflicts of interest and conclusions about neuraminidase inhibitors for influenza: an analysis of systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine 2014;161(7):513‐8. - PubMed
Faggion 2014 {published data only}
-
- Faggion CM Jr, Atieh M, Zanicotti DG. Reporting of sources of funding in systematic reviews in periodontology and implant dentistry. British Dental Journal 2014;216(3):109‐12. - PubMed
Finnerup 2015 {published data only}
Fleurence 2010 {published data only}
-
- Fleurence RL, Spackman DE, Hollenbeak C. Does the funding source influence the results in economic evaluations? A case study in bisphosphonates for the treatment of osteoporosis. Pharmacorconomics 2010;28(4):295‐306. - PubMed
Friedman 2004 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Fu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Fu R, Selph S, McDonagh M, Peterson K, Tiwari A, Chou R, et al. Effectiveness and harms of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein‐2 in spine fusion: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;158(12):890‐902. - PubMed
Fukunaga 2014 {published data only}
Furuse 2011 {published data only}
-
- Furuse J, Okusaka T, Bridgewater J, Taketsuna M, Wasan H, Koshiji M, et al. Lessons from the comparison of two randomized clinical trials using gemcitabine and cisplatin for advanced biliary tract cancer. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 2011;80(1):31‐9. - PubMed
Garattini 2010 {published data only}
-
- Garattini L, Koleva D, Casadei G. Modeling in pharmacoeconomic studies: funding sources and outcomes. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2010;26(3):330‐3. - PubMed
Garrison 2010 {published data only}
Gasparyan 2013 {published data only}
Gerrald 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gerrald KR, Malone RM, Shillida BB. Clinical benefit of self‐monitoring of blood glucose is uncertain for non–insulin‐treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Clinical Diabetes 2012;28(3):121‐3.
Gewandter 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gewandter JS, Smith SM, McKeown A, Burke LB, Hertz SH, Hunsinger M, et al. Reporting of primary analyses and multiplicity adjustment in recent analgesic clinical trials: ACTTION systematic review and recommendations. Pain 2014;155(3):461‐6. - PubMed
Glick 2006 {published data only}
-
- Glick N, MacDonald I, Knoll G, Brabant A, Gourishankar S. Factors associated with publication following presentation at a transplantation meeting. American Journal of Transplantation 2006;6(3):552‐6. - PubMed
Glujovsky 2012 {published data only}
-
- Glujovsky D, Riestra B, Coscia A, Boggino C, Comande D, Ciapponi A. Assessment of research quality in major infertility journals. Fertility and Sterility 2012;98(6):1539‐43. - PubMed
Goswami 2014 {published data only}
Graham 2012 {published data only}
-
- Graham CN, Mauskopf JA, Lawson AH, Ascher‐Svanum H, Bruhn D. Updating and confirming an industry‐sponsored pharmacoeconomic model: comparing two antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia. Value in Health 2012;15(1):55‐64. - PubMed
Grillo‐Ardila 2014 {published data only}
Guaiana 2013 {published data only}
Guo 2013 {published data only}
-
- Guo SW, Evers JL. Lack of transparency of clinical trials on endometriosis. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2013;121(6):1281‐90. - PubMed
Guo 2014 {published data only}
-
- Guo SW. An overview of the current status of clinical trials on endometriosis: issues and concerns. Fertility and Sterility 2014;101(1):183‐190.e4. - PubMed
Hall 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hall R, Antueno C, Webber A, Canadian Research Ethics Board. Publication bias in the medical literature: A review by a Canadian Research Ethics Board. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 2007;54(5):380‐8. - PubMed
Hartling 2011 {published data only}
Hartung 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hartung DM, Zarin DA, Guise JM, McDonagh M, Paynter R, Helfand M. Reporting discrepancies between the ClinicalTrials.gov results database and peer‐reviewed publications. Annals of Internal Medicine 2014;160(7):477‐83. - PMC - PubMed
Hashmi 2014 {published data only}
Hill 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hill CL, Buchbinder R, Osborne R. Quality of reporting of randomized clinical trials in abstracts of the 2005 annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Journal of Rheumatology 2007;34(12):2476‐80. - PubMed
Hodgson 2014 {published data only}
Hughes 2014 {published data only}
Ioannidis 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ioannidis JP, Karassa FB, Druyts E, Thorlund K, Mills EJ. Biologic agents in rheumatology: unmet issues after 200 trials and $200 billion sales. Nature Reviews Rheumatology 2013;9(11):665‐73. - PubMed
Ipser 2015 {published data only}
Jagsi 2009 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Jagsi R, Sheets N, Jankovic A, Motomura AR, Amarnath S, Ubel PA. Frequency, nature, effects, and correlates of conflicts of interest in published clinical cancer research. Cancer 2009;115(12):2783‐91. - PubMed
Jang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jang S, Chae YK, Haddad T, Majhail NS. Conflict of interest in economic analyses of aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer: a systematic review. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2010;121(2):273‐9. - PubMed
Jefferson 2012 {published data only}
Jefferson 2014 {published data only}
Jones 2013 {published data only}
Kaiser 2012 {published data only}
Khan 2008 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Khan SN, Mermer MJ, Myers E, Sandhu HS. The roles of funding source, clinical trial outcome, and quality of reporting in orthopedic surgery literature. American Journal of Orthopedics 2008;37(12):E205‐12. - PubMed
Kjaergard 1999 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Kjaergard LL, Nikolova D, Gluud C. Randomized clinical trials in HEPATOLOGY: predictors of quality. Hepatology 1999;30(5):1134‐8. - PubMed
Komossa 2011 {published data only}
Krauth 2014 {published data only}
Krzyzanowska 2003 {published data only}
-
- Krzyzanowska MK, Pintilie M, Tannock IF. Factors associated with failure to publish large randomized trials presented at an oncology meeting. JAMA 2003;290(4):495‐501. - PubMed
Kulier 2004 {published data only}
Kulkarni 2007 {published data only}
Lai 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Lai R, Chu R, Fraumeni M, Thabane L. Quality of randomized controlled trials reporting in the primary treatment of brain tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006; Vol. 24, issue 7:1136‐44. - PubMed
Lawrie 2011 {published data only}
Leopold 2003 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Leopold SS, Warme WJ, Fritz Braunlich E, Shott S. Association between funding source and study outcome in orthopaedic research. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 2003;415:293‐301. - PubMed
Lethaby 2013 {published data only}
Leucht 2009a {published data only}
-
- Leucht S, Corves C, Arbter D, Engel RR, Li C, Davis JM. Second‐generation versus first‐generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia: a meta‐analysis. Lancet 2009;373(9657):31‐41. - PubMed
Leucht 2009b {published data only}
-
- Leucht S, Komossa K, Rummel‐Kluge C, Corves C, Hunger H, Schmid F, et al. A meta‐analysis of head‐to‐head comparisons of second‐generation antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 2009;166(2):152‐63. - PubMed
Li 2013 {published data only}
-
- Li XQ, Yang GL, Tao KM, Zhang HQ, Zhou QH, Ling CQ. Comparison of registered and published primary outcomes in randomized controlled trials of gastroenterology and hepatology. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2013;48(12):1474‐83. - PubMed
Lopez 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lopez J, Prifogle E, Nyame TT, Milton J, May JW Jr. The impact of conflicts of interest in plastic surgery: an analysis of acellular dermal matrix, implant‐based breast reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2014;133(6):1328‐34. - PubMed
Lundh 2012 {published data only}
Lunn 2014 {published data only}
Magni 2013 {published data only}
Manzoli 2011 {published data only}
Manzoli 2014 {published data only}
-
- Manzoli L, Flacco ME, D'Addario M, Capasso L, Vito C, Marzuillo C, et al. Non‐publication and delayed publication of randomized trials on vaccines: survey. BMJ 2014;348:g3058. - PubMed
McIlvennan 2014 {published data only}
McLennan 2008 {published data only}
-
- McLennan M, Leong FC, Steele A, Harris J. The influence of industry sponsorship on the acceptance of abstracts and their publication. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2008;198(5):579.e1‐4. - PubMed
Montedori 2011 {published data only}
Montori 2005 {published data only}
-
- Montori VM, Devereaux PJ, Adhikari NK, Burns KE, Eggert CH, Briel M, et al. Randomized trials stopped early for benefit: a systematic review. JAMA 2005;294(17):2203‐9. - PubMed
Moteshafi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Moteshafi H, Zhornitsky S, Brunelle S, Stip E. Comparing tolerability of olanzapine in schizophrenia and affective disorders: a meta‐analysis. Drug Safety 2012;35(10):819‐36. - PubMed
Nkansah 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nkansah N, Nguyen T, Iraninezhad H, Bero L. Randomized trials assessing calcium supplementation in healthy children: relationship between industry sponsorship and study outcomes. Public Health Nutrition 2009;12(10):1931‐7. - PubMed
Okike 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Okike K, Kocher MS, Mehlman CT, Bhandari M. Conflict of interest in orthopaedic research: An association between findings and funding in scientific presentations. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 2007;89(3):608‐13. - PubMed
Okike 2008 {published data only}
Peura 2012 {published data only}
-
- Peura PK, Martikainen JA, Purmonen TT, Turunen JH. Sponsorship‐related outcome selection bias in published economic studies of triptans: systematic review. Medical Decision Making 2012;32(2):237‐45. - PubMed
Phillips 2012 {published data only}
-
- Phillips JL, Wassersug RJ, McLeod DL. Systemic bias in the medical literature on androgen deprivation therapy and its implication to clinical practice. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2012;66(12):1189‐96. - PubMed
Polyzos 2011 {published data only}
Probst 2014 {published data only}
Procyshyn 2004 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Procyshyn RM, Chau A, Fortin P, Jenkins W. Prevalence and outcomes of pharmaceutical industry‐sponsored clinical trials involving clozapine, risperidone, or olanzapine. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 2004;49(9):601‐6. - PubMed
Purgato 2014 {published data only}
Radecki 2011 {published data only}
Ramagopalan 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ramagopalan S, Skingsley AP, Handunnetthi L, Klingel M, Magnus D, Pakpoor J, et al. Prevalence of primary outcome changes in clinical trials registered on ClinicalTrials.gov: a cross‐sectional study. F1000Research 2014;3:77. - PMC - PubMed
Rattehalli 2010 {published data only}
Roach 2008 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Roach JW, Skaggs DL, Sponseller PD, Macleod LM. Is research presented at the scoliosis research society annual meeting influenced by industry funding?. Spine 2008;33(20):2208‐12. - PubMed
Sanossian 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sanossian N, Ohanian AG, Saver JL, Kim LI, Ovbiagele B. Frequency and determinants of nonpublication of research in the stroke literature. Stroke 2006;37:2588‐92. - PubMed
Sawata 2011 {published data only}
Schott 2010 {published data only}
-
- Schott G, Pachl H, Ludwig WD. The relation between publication bias and clinical trials funding [Publikationsbias in Abhangigkeit von der Art der Finanzierung bei klinischen Studien.]. Zeitschrift fur Evidenz, Fortbildung und Qualitat im Gesundheitswesen 2010;104(4):314‐22. - PubMed
Schott 2010a {published data only}
-
- Schott G, Pachl H, Limbach U, Gundert‐Remy U, Ludwig WD, Lieb K. The financing of drug trials by pharmaceutical companies and its consequences. Part 1: a qualitative, systematic review of the literature on possible influences on the findings, protocols, and quality of drug trials. Deutsches Arzteblatt international 2010;107(16):279‐85. - PMC - PubMed
Schott 2013 {published data only}
Shah 2005 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Shah RV, Albert TJ, Bruegel‐Sanchez V, Vaccaro AR, Hilibrand AS, Grauer JN. Industry support and correlation to study outcome for papers published in spine. Spine 2005;30(9):1099‐104. - PubMed
Shamliyan 2012 {published data only}
-
- Shamliyan TA, Kane RL, Wyman J, Sainfort F. Results availability from clinical research of female urinary incontinence. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2012;31(1):22‐9. - PubMed
Shen 2014 {published data only}
-
- Shen C, Chien CR, Geynisman DM, Smieliauskas F, Shih YC. A review of economic impact of targeted oral anticancer medications. Expert Review of Pharmacoeconomics & Outcomes Research 2014;14(1):45‐69. - PubMed
Stamatakis 2013 {published data only}
-
- Stamatakis E, Weiler R, Ioannidis JP. Undue industry influences that distort healthcare research, strategy, expenditure and practice: a review. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2013;43(5):469‐75. - PubMed
Strupp 2010 {published data only}
-
- Strupp M. Pharmacotherapy: why industry‐sponsored trials are more often positive and other useful information. Journal of Neurology 2010;257(2):309‐12. - PubMed
Sun 2011 {published data only}
Sun 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sun GH, Houlton JJ, MacEachern MP, Bradford CR, Hayward RA. Influence of study sponsorship on head and neck cancer randomized trial results. Head & Neck 2013;35(10):1515‐20. - PubMed
Thirugnanam 2012 {published data only}
Thomas 2008 {published data only}
Thomson 2010 {published data only}
Valachis 2012 {published data only}
-
- Valachis A, Polyzos NP, Nearchou A, Lind P, Mauri D. Financial relationships in economic analyses of targeted therapies in oncology. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2012;30(12):1316‐20. - PubMed
van Lent 2013 {published data only}
Wang 2010 {published data only}
Watanabe 2010 {published data only}
-
- Watanabe N, Omori IM, Nakagawa A, Cipriani A, Barbui C, McGuire H, et al. Safety reporting and adverse‐event profile of mirtazapine described in randomized controlled trials in comparison with other classes of antidepressants in the acute‐phase treatment of adults with depression: systematic review and meta‐analysis. CNS Drugs 2010;24(1):35‐53. - PubMed
Yao 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Yao F, Singer M, Rosenfeld RM. Randomized controlled trials in otolaryngology journals. Otolaryngology‐Head and Neck Surgery 2007;137(4):539‐44. - PubMed
Yaphe 2001 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Yaphe J, Edman R, Knishkowy B, Herman J. The association between funding by commercial interests and study outcome in randomized controlled drug trials. Family Practice 2001;18(6):565‐8. - PubMed
Yuan 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yuan JC, Shyamsunder N, Barao VA, Lee DJ, Sukotjo C. Publication bias in five dental implant journals: an observation from 2005 to 2009. International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 2011;26(5):1024‐32. - PubMed
Yue 2013 {published data only}
Zani 2011 {published data only}
Additional references
Bekelman 2003
-
- Bekelman JE, Li Y, Gross CP. Scope and impact of financial conflicts of interest in biomedical research: a systematic review. JAMA 2003;289(4):454‐65. - PubMed
Bero 1996
-
- Bero LA, Rennie D. Influences on the quality of published drug studies. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 1996;12(2):209‐37. - PubMed
Boutron 2010
-
- Boutron I, Dutton S, Ravaud P, Altman DG. Reporting and interpretation of randomized controlled trials with statistically nonsignificant results for primary outcomes. JAMA 2010;303(20):2058‐64. - PubMed
Chan 2004
-
- Chan AW, Hróbjartsson A, Haahr MT, Gøtzsche PC, Altman DG. Empirical evidence for selective reporting of outcomes in randomized trials: comparison of protocols to published articles. JAMA 2004;291(20):2457‐65. - PubMed
Christensen 2012
-
- Christensen M, Knop FK. The unobtainable placebo: control of independent clinical research by industry?. Lancet 2012; Vol. 379, issue 9810:30. - PubMed
DeAngelis 2004
-
- DeAngelis CD, Drazen JM, Frizelle FA, Haug C, Hoey J, Horton R, et al. Clinical trial registration: a statement from the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. JAMA 2004; Vol. 292, issue 11:1363‐4. - PubMed
DeAngelis 2010
-
- DeAngelis CD, Fontanarosa PB. The importance of independent academic statistical analysis. Biostatistics 2010;11(3):383‐4. - PubMed
Devereaux 2001
-
- Devereaux PJ, Manns BJ, Ghali WA, Quan H, Lacchetti C, Montori VM, et al. Physician interpretations and textbook definitions of blinding terminology in randomized controlled trials. JAMA 2001;285(15):2000‐3. - PubMed
Djulbegovic 2003
-
- Djulbegovic B, Cantor A, Clarke M. The importance of preservation of the ethical principle of equipoise in the design of clinical trials: relative impact of the methodological quality domains on the treatment effect in randomized controlled trials. Accountability in Research 2003;10(4):301‐15. - PubMed
Doshi 2012
-
- Doshi P, Jones M, Jefferson T. Rethinking credible evidence synthesis. BMJ 2012;344:d7898. - PubMed
Doshi 2013
Dunn 2013
Dwan 2008
Dwan 2011
Estellat 2012
-
- Estellat C, Ravaud P. Lack of head‐to‐head trials and fair control arms: randomized controlled trials of biologic treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. Archives of Internal Medicine 2012;172(3):237‐44. - PubMed
Fugh‐Berman 2010
Furukawa 2004
Godlee 2009
-
- Godlee F. We want raw data, now. BMJ 2009;339:b5405.
Golder 2008
Golder 2016
Goodman 2011
-
- Goodman S, Dickersin K. Metabias: a challenge for comparative effectiveness research. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011; Vol. 155, issue 1:61‐2. - PubMed
Gøtzsche 2011
Hart 2012
-
- Hart B, Lundh A, Bero L. Effect of reporting bias on meta‐analyses of drug trials: reanalysis of meta‐analyses. BMJ 2012;344:d7202. - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Johansen 1999
-
- Johansen HK, Gøtzsche PC. Problems in the design and reporting of trials of antifungal agents encountered during meta‐analysis. JAMA 1999;282(18):1752‐9. - PubMed
Johnson 2016
Jüni 1999
-
- Juni P, Witschi A, Bloch R, Egger M. The hazards of scoring the quality of clinical trials for meta‐analysis. JAMA 1999;282(11):1054‐60. - PubMed
Katz 2006
-
- Katz KA, Karlawish JH, Chiang DS, Bognet RA, Propert KJ, Margolis DJ. Prevalence and factors associated with use of placebo control groups in randomized controlled trials in psoriasis: a cross‐sectional study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2006;55(5):814‐22. - PubMed
Kirkham 2010
-
- Kirkham JJ, Dwan KM, Altman DG, Gamble C, Dodd S, Smyth R, et al. The impact of outcome reporting bias in randomised controlled trials on a cohort of systematic reviews. BMJ 2010;340:c365. - PubMed
Krleza‐Jeric 2005
Lathyris 2010
-
- Lathyris DN, Patsopoulos NA, Salanti G, Ioannidis JP. Industry sponsorship and selection of comparators in randomized clinical trials. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2010;40(2):172‐82. - PubMed
Le Noury 2015
Lexchin 2012
-
- Lexchin J. Those who have the gold make the evidence: how the pharmaceutical industry biases the outcomes of clinical trials of medications. Science and Engineering Ethics 2012;18(2):247‐61. - PubMed
Lundh 2008
MAGICapp [Computer program]
-
- MAGIC authoring and publication platform (MAGICapp) for improving patient care through guidelines, evidence summaries and decision aids that we can all trust, use and share. Version Accessed May 24, 2016.
Mandelkern 1999
-
- Mandelkern M. Manufacturer support and outcome. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1999; Vol. 60, issue 2:122‐3. - PubMed
McGauran 2010
Melander 2003
Moses 2015
-
- Moses H 3rd, Matheson DH, Cairns‐Smith S, George BP, Palisch C, Dorsey ER. The anatomy of medical research: US and international comparisons. JAMA 2015;313(2):174‐89. - PubMed
Oxman 1991
-
- Oxman AD, Guyatt GH, Singer J, Goldsmith CH, Hutchison BG, Milner RA, et al. Agreement among reviewers of review articles. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1991;44(1):91‐8. - PubMed
Palmer 2003
-
- Palmer RH. Results of clinical trials sponsored by for‐profit vs nonprofit entities. JAMA 2003; Vol. 290, issue 23:3070. - PubMed
PhRMA 2008
-
- PhRMA. Pharmaceutical marketing in perspective: its value and role as one of many factors informing prescribing. http://www.phrma.org/issues/sales‐marketing (accessed 22 February 2012).
Pildal 2007
-
- Pildal J, Hróbjartsson A, Jørgensen KJ, Hilden J, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC. Impact of allocation concealment on conclusions drawn from meta‐analyses of randomized trials. International Journal of Epidemiology 2007;36(4):847‐57. - PubMed
Potthast 2014
Psaty 2008
-
- Psaty BM, Kronmal RA. Reporting mortality findings in trials of rofecoxib for Alzheimer disease or cognitive impairment: a case study based on documents from rofecoxib litigation. JAMA 2008;299(15):1813‐7. - PubMed
Psaty 2010
-
- Psaty BM, Prentice RL. Minimizing bias in randomized trials: the importance of blinding. JAMA 2010;304(7):793‐4. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3.5. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rising 2008
Rosefsky 2003
-
- Rosefsky JB. Results of clinical trials sponsored by for‐profit vs nonprofit entities. JAMA 2003; Vol. 290, issue 23:3070‐1. - PubMed
Roseman 2011
-
- Roseman M, Milette K, Bero LA, Coyne JC, Lexchin J, Turner EH, et al. Reporting of conflicts of interest in meta‐analyses of trials of pharmacological treatments. JAMA 2011;305(10):1008‐17. - PubMed
Roseman 2012
Ross 2008
-
- Ross JS, Hill KP, Egilman DS, Krumholz HM. Guest authorship and ghostwriting in publications related to rofecoxib: a case study of industry documents from rofecoxib litigation. JAMA 2008;299(15):1800‐12. - PubMed
Safer 2002
-
- Safer DJ. Design and reporting modifications in industry‐sponsored comparative psychopharmacology trials. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 2002;190(9):583‐92. - PubMed
Schwartz 2016
-
- Schwartz LM, Woloshin S, Zheng E, Tse T, Zarin DA. ClinicalTrials.gov and Drugs@FDA: A comparison of results reporting for new drug approval trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2016;165(6):421‐30. - PMC - PubMed
Shea 2007
Sismondo 2008a
-
- Sismondo S. Pharmaceutical company funding and its consequences: a qualitative systematic review. Contemporay Clinical Trials 2008;29(2):109‐13. - PubMed
Sismondo 2008b
-
- Sismondo S. How pharmaceutical industry funding affects trial outcomes: causal structures and responses. Social Science & Medicine 2008;66(9):1909‐14. - PubMed
Steinman 2006
-
- Steinman MA, Bero LA, Chren M‐M, Landefeld S. The promotion of gabapentin: an analysis of internal industry documents. Annals of Internal Medicine 2006;145(4):284‐93. - PubMed
Stelfox 1998
-
- Stelfox HT, Chua G, O'Rourke K, Detsky AS. Conflict of interest in the debate over calcium‐channel antagonists. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338(2):101‐6. - PubMed
Thomas 2002
-
- Thomas PS, Tan KS, Yates DH. Sponsorship, authorship, and accountability. Lancet 2002; Vol. 359, issue 9303:351. - PubMed
Tuech 2005
-
- Tuech JJ, Moutel G, Pessaux P, Thoma V, Schraub S, Herve C. Disclosure of competing financial interests and role of sponsors in phase III cancer trials. European Journal of Cancer 2005;41(15):2237‐40. - PubMed
Vandvik 2013
-
- Vandvik PO, Brandt L, Alonso‐Coello P, Treweek S, Akl EA, Kristiansen A, et al. Creating clinical practice guidelines we can trust, use, and share: a new era is imminent. Chest 2013;144(2):381‐9. - PubMed
Vedula 2009
-
- Vedula SS, Bero L, Scherer RW, Dickersin K. Outcome reporting in industry‐sponsored trials of gabapentin for off‐label use. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;361(20):1963‐71. - PubMed
Wyatt 1991
-
- Wyatt J. Use and sources of medical knowledge. Lancet 1991;338(8779):1368‐73. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Lexchin 2003
Lundh 2011
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

