Milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 inhibits periodontitis in non-human primates and its gingival crevicular fluid levels can differentiate periodontal health from disease in humans
- PMID: 28207941
- PMCID: PMC5433891
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12707
Milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 inhibits periodontitis in non-human primates and its gingival crevicular fluid levels can differentiate periodontal health from disease in humans
Abstract
Aim: We have previously shown that the secreted glycoprotein milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 (MFG-E8) has anti-inflammatory and anti-osteoclastogenic properties. Our objective was to investigate the potential of MFG-E8 as a diagnostic or therapeutic agent in periodontitis.
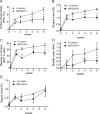
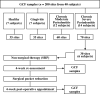
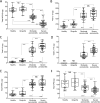
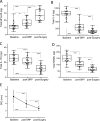
Materials and methods: Periodontitis was induced in non-human primates (NHPs) by placing ligatures around posterior teeth on both halves of the mandible for a split-mouth design: one side was treated with MFG-E8-Fc and the other with Fc control. Disease was assessed by clinical periodontal examinations, radiographic analysis of bone loss, and analysis of cytokine mRNA expression in gingival biopsy samples. Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) was collected from human healthy volunteers or subjects with gingivitis, chronic moderate periodontitis, or chronic severe periodontitis. Additionally, GCF was collected from a subset of severe periodontitis patients following scaling and root planing (SRP) and after pocket reduction surgery. GCF was analysed to quantify MFG-E8 and periodontitis-relevant cytokines using multiplex assays.
Results: In NHPs, sites treated with MFG-E8-Fc exhibited significantly less ligature-induced periodontal inflammation and bone loss than Fc control-treated sites. In humans, the GCF levels of MFG-E8 were significantly higher in health than in periodontitis, whereas the reverse was true for the proinflammatory cytokines tested. Consistently, MFG-E8 was elevated in GCF after both non-surgical (SRP) and surgical periodontal treatment of periodontitis patients.
Conclusion: MFG-E8 is, in principle, a novel therapeutic agent and biomarker of periodontitis.
Keywords: cytokines; inflammation; milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8; non-human primates; periodontitis.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
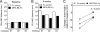

References
-
- Ait-Oufella H, Kinugawa K, Zoll J, Simon T, Boddaert J, Heeneman S, Blanc-Brude O, Barateau V, Potteaux S, Merval R, Esposito B, Teissier E, Daemen MJ, Leseche G, Boulanger C, Tedgui A, Mallat Z. Lactadherin deficiency leads to apoptotic cell accumulation and accelerated atherosclerosis in mice. Circulation. 2007;115:2168–2177. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar S, Wang X, Bu HF, Tan XD. Role of MFG-E8 in Protection of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function and Attenuation of Intestinal Inflammation. In: Wang P, editor. MFG-E8 and Inflammation. New York: Springer; 2014. pp. 55–64.
-
- Albus E, Sinningen K, Winzer M, Thiele S, Baschant U, Hannemann A, Fantana J, Tausche AK, Wallaschofski H, Nauck M, Volzke H, Grossklaus S, Chavakis T, Udey MC, Hofbauer LC, Rauner M. Milk Fat Globule-Epidermal Growth Factor 8 (MFG-E8) Is a Novel Anti-inflammatory Factor in Rheumatoid Arthritis in Mice and Humans. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31:596–605. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armitage GC. Development of a classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions. Ann Periodontol. 1999;4:1–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

