Altered olfactory processing and increased insula activity in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: An fMRI study
- PMID: 28208068
- PMCID: PMC5373557
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2017.01.012
Altered olfactory processing and increased insula activity in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: An fMRI study
Abstract
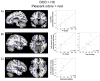
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) patients show increased insula activation to disgust-inducing images compared to healthy controls (HC). We explored whether this disgust reactivity was also present in the olfactory domain by conducting the first fMRI study of olfaction in OCD. Neural activation in response to pleasant and unpleasant odors (vs. unscented air) was investigated in 15 OCD and 15 HC participants using fMRI. OCD participants (vs. HC) had increased left anterior insula activation to unpleasant odors (vs. unscented air), which positively correlated with their disgust sensitivity and ratings of the unpleasantness and intensity of those odors. OCD participants (vs. HC) showed increased activation of caudate nucleus and left anterior and posterior insula to pleasant odors (vs. unscented air), which positively correlated with their OCD symptom severity, trait anxiety, frequency of feeling disgust, and odor intensity ratings. OCD participants had increased anterior insula activation to both pleasant and unpleasant odors, which correlated with their OCD symptoms, anxiety, disgust sensitivity, and frequency of feeling disgust. OCD patients might have a negative cognitive bias and experience all stimuli, regardless of valence, as being more unpleasant than healthy people. These findings further elucidate the neural underpinnings of OCD and may contribute to more effective treatments.
Keywords: Anxiety; Disgust; Emotion; OCD; Odor; Olfaction; Sensory.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Heather A. Berlin, Dr. Emily R. Stern, Dr. Johnny Ng, Sam Zhang, David Rosenthal, Rachel Turetzky, and Dr. Cheuk Tang report no conflicts of interest. Dr..Wayne Goodman reports research funding from Roche, Simon Foundation and NIMH.
Figures


References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic criteria from DSM-IV-TR. Washington, D.C: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
-
- Augustine JR. Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1996;22:229–244. - PubMed
-
- Barnett R, Maruff P, Purcell R, Wainwright K, Kyrios M, Brewer W, et al. Impairment of olfactory identification in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychol Med. 1999;29:1227–1233. - PubMed
-
- Berle D, Phillips ES. Disgust and obsessive-compulsive disorder: An update. Psychiatry. 2006;69:228–238. - PubMed
-
- Berlin HA, Rolls ET, Iversen SD. Borderline personality disorder, impulsivity, and the orbitofrontal cortex. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162:2360–2373. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

