Emergence of TNIK inhibitors in cancer therapeutics
- PMID: 28208209
- PMCID: PMC5448614
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13203
Emergence of TNIK inhibitors in cancer therapeutics
Abstract
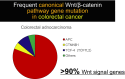
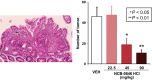
The outcome of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer remains unsatisfactory. To improve patient prognosis, it will be necessary to identify new drug targets based on molecules that are essential for colorectal carcinogenesis, and to develop therapeutics that target such molecules. The great majority of colorectal cancers (>90%) have mutations in at least one Wnt signaling pathway gene. Aberrant activation of Wnt signaling is a major force driving colorectal carcinogenesis. Several therapeutics targeting Wnt pathway molecules, including porcupine, frizzled receptors and tankyrases, have been developed, but none of them have yet been incorporated into clinical practice. Wnt signaling is most frequently activated by loss of function of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor suppressor gene. Restoration of APC gene function does not seem to be a realistic therapeutic approach, and, therefore, only Wnt signaling molecules downstream of the APC gene product can be considered as targets for pharmacological intervention. Traf2 and Nck-interacting protein kinase (TNIK) was identified as a regulatory component of the β-catenin and T-cell factor-4 (TCF-4) transcriptional complex. Several small-molecule compounds targeting this protein kinase have been shown to have anti-tumor effects against various cancers. An anthelmintic agent, mebendazole, was recently identified as a selective inhibitor of TNIK and is under clinical evaluation. TNIK regulates Wnt signaling in the most downstream part of the pathway, and its pharmacological inhibition seems to be a promising therapeutic approach. We demonstrated the feasibility of this approach by developing a small-molecule TNIK inhibitor, NCB-0846.
Keywords: TNIK; Cancer stem cell; Wnt signaling; colorectal cancer; molecular targeted therapy.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Therapeutic targets in the Wnt signaling pathway: Feasibility of targeting TNIK in colorectal cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Dec;156:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.10.009. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26542362 Review.
-
TNIK inhibition abrogates colorectal cancer stemness.Nat Commun. 2016 Aug 26;7:12586. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12586. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27562646 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Insight into TNIK Inhibition.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13010. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113010. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Wnt signaling pathway in colorectal cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016;20(4):419-29. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2016.1098619. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016. PMID: 26439805 Review.
-
Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase is essential for Wnt signaling and colorectal cancer growth.Cancer Res. 2010 Jun 15;70(12):5024-33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0306. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20530691
Cited by
-
Direct conversion of osteosarcoma to adipocytes by targeting TNIK.JCI Insight. 2021 Feb 8;6(3):e137245. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.137245. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33400690 Free PMC article.
-
Mebendazole as a Candidate for Drug Repurposing in Oncology: An Extensive Review of Current Literature.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 31;11(9):1284. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091284. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31480477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De Novo Discovery of Thiopeptide Pseudo-natural Products Acting as Potent and Selective TNIK Kinase Inhibitors.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Nov 9;144(44):20332-20341. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c07937. Epub 2022 Oct 25. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 36282922 Free PMC article.
-
TNIK influence the effects of antipsychotics on Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Nov;238(11):3283-3292. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05943-3. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34350475
-
A Cell Model Suitable for a High-Throughput Screening of Inhibitors of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 11;9:1160. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01160. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30364258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kato H, Sobue T, Katanoda K et al Editorial Board of the Cancer Statistics in Japan. Cancer statistics in Japan 2007. Tokyo: Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research (FPCF), 2007.
-
- Okuno K. Surgical treatment for digestive cancer. Current issues – Colon cancer. Dig Surg 2007; 24: 108–14. - PubMed
-
- Koutras AK, Starakis I, Kyriakopoulou U et al Targeted therapy in colorectal cancer: current status and future challenges. Curr Med Chem 2011; 18: 1599–612. - PubMed
-
- Omura K. Advances in chemotherapy against advanced or metastatic colorectal cancer. Digestion 2008; 77(Suppl 1): 13–22. - PubMed
-
- Grothey A, Van Cutsem E, Sobrero A et al Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): an international, multicentre, randomised, placebo‐controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013; 381: 303–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

