The effect of hypericum perforatum on kidney ischemia/reperfusion damage
- PMID: 28209087
- PMCID: PMC6014337
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2017.1287734
The effect of hypericum perforatum on kidney ischemia/reperfusion damage
Abstract
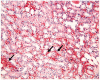
It has been revealed in recent studies that Hypericum Perforatum (HP) is influential on cancer, inflammatory diseases, bacterial and viral diseases, and has neuroprotective and antioxidant properties. In this study, we investigated the effect of HP, which is known to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, on kidney I/R damage. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into three groups, and each of the groups had eight rats: The Control Group; the Ischemia/Reperfusion (I/R) Group; and the IR + HP Group which was treated with 50 mg/kg of HP. The right kidneys of the rats were removed, and the left kidney developed ischemia during the 45th min, and reperfusion occurred in the following 3rd h. The histopathological findings and also the level of Malondialdehyde (MDA), Glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) enzyme activations in the renal tissues were measured. Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), Creatinin (Cre) from serum samples were determined. The levels of BUN, Cre, and kidney tissue MDA increased at a significant level, and the SOD, CAT, and GSH-PX enzyme activity decreased at a significant level in the I/R group, compared with the Control Group (p < 0.05). In the I/R + HP group, the levels of MDA decreased at a significant level compared to the I/R group, while the SOD, CAT, and GSH-PX activity increased (p < 0.05). In histopathological examinations, it was observed that the tubular dilatation and epithelial desquamation regressed in the IR + HP Group when compared with the I/R Group. It has been shown with the histological and biochemical results in this study that HP is protective against acute renal I/R.
Keywords: Kidney; hypericum perforatum; ischemia-reperfusion; oxidative stress; rat.
Figures
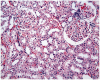
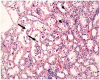
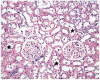
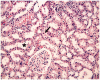
Similar articles
-
Effect of Camellia sinensis, Hypericum perforatum and Urtica dioica on kidney and liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2019 Jun 30;65(5):79-86. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2019. PMID: 31304911
-
[Protective effect of phloroglucinol on renal ischemia and reperfusion injury].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 Oct 18;47(5):743-8. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015. PMID: 26474609 Chinese.
-
The effect of dexmedetomidine against oxidative and tubular damage induced by renal ischemia reperfusion in rats.Ren Fail. 2015 May;37(4):704-8. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2015.1011550. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Ren Fail. 2015. PMID: 25687385
-
The effect of Rheum ribes L. on oxidative stress in diabetic rats.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 15:/j/jbcpp.ahead-of-print/jbcpp-2020-0058/jbcpp-2020-0058.xml. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2020-0058. Online ahead of print. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32813675 Review.
-
A review of the protective effects of quercetin-rich natural compounds for treating ischemia-reperfusion injury.Biotech Histochem. 2022 May;97(4):237-246. doi: 10.1080/10520295.2021.1937701. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Biotech Histochem. 2022. PMID: 34157912 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of renal cold ischemia-reperfusion injury with intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging and blood oxygenation level-dependent MRI in a rat model.Front Physiol. 2023 May 22;14:1159741. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1159741. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37284547 Free PMC article.
-
A study on the effect of Hypericum perforatum L. extract on vanadium toxicity in Allium cepa L.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 18;14(1):28486. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79535-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39557924 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of St. John's Wort and Its Components Hyperforin and Hypericin against Diabetes through Inhibition of Inflammatory Signaling: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 30;21(21):8108. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218108. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33143088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plants with Therapeutic Potential for Ischemic Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 23;2022:6807700. doi: 10.1155/2022/6807700. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35656467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Great Healing Potential Hidden in Plant Preparations of Antioxidant Properties: A Return to Nature?Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Oct 9;2020:8163868. doi: 10.1155/2020/8163868. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33101592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bucuvic EM, Ponce D, Balbi AL.. Risk factors for mortality in acute kidney injury. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2011;57:158–163. - PubMed
-
- Ozer Sehirli A, Sener G, Ercan F.. Protective effects of pycnogenol against ischemia reperfusion-induced oxidative renal injury in rats. Ren Fail. 2009;31:690–697. - PubMed
-
- Wang ZS, Liu XH, Wang M, et al. . Metformin attenuated the inflammation after renal ischemia/reperfusion and suppressed apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cell in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 2015;30:617–623. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
