miR-296 inhibits the metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer by targeting S100A4
- PMID: 28209128
- PMCID: PMC5311719
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3121-z
miR-296 inhibits the metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer by targeting S100A4
Abstract
Background: Dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) is actively involved in the pathogenesis and tumorigenicity of colorectal cancer (CRC). miR-296 was found to play either oncogenic or tumor suppressive role in human cancers. However, the status of miR-296 and its function in CRC remain unknown.
Methods: The expression of miR-296 was confirmed by qRT-PCR in CRC tissues and cells, and its level was altered by corresponding miRNA vectors. Wound healing and Transwall assays were performed to detect the migration and invasion of CRC cells. The levels of proteins were measured using immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence.
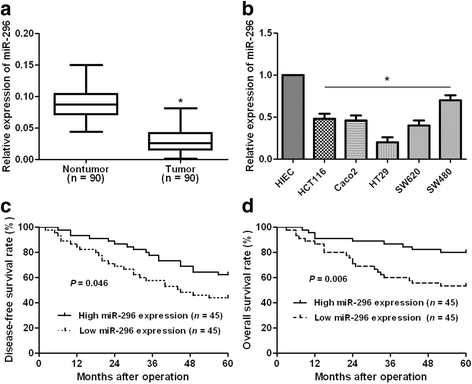
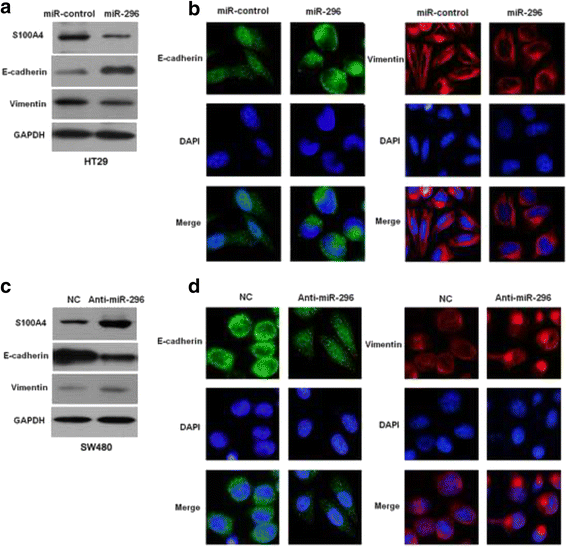
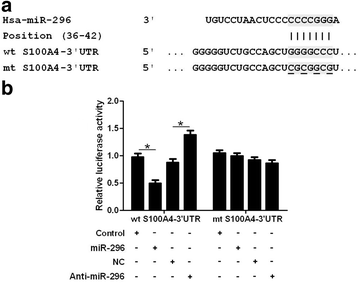
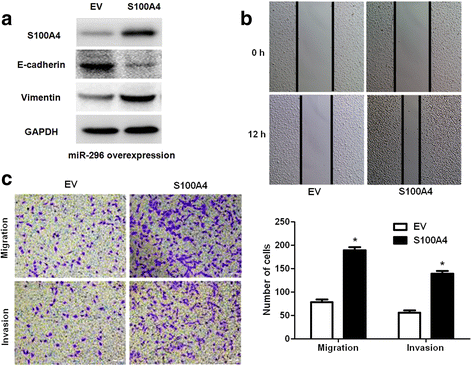
Results: Underexpression of miR-296 was disclosed in CRC tissues and cells. Its decreased level was evidently correlated with adverse clinical parameters and poor prognosis of CRC patients. In vitro experiments indicated that miR-296 inhibited CRC cell migration and invasion. Mechanically, miR-296 inhibited the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of CRC cells. A negative correlation between miR-296 and S100A4 expression was observed in CRC tissues. Luciferase reporter assays indicated that miR-296 inversely regulated the luciferase activity of 3'-UTR of S100A4. Herein, S100A4 was found to be a downstream molecule of miR-296 in CRC. Furthermore, S100A4 mediated the anti-metastatic effects of miR-296 on EMT, migration and invasion of CRC cells.
Conclusions: miR-296 functions as an anti-metastatic factor mainly by suppressing S100A4 in CRC. It potentially acts as a prognostic predictor and a drug-target for CRC patients.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Metastasis; S100A4; miR-296.
Figures




Similar articles
-
miR-187-3p inhibits the metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting S100A4.Cancer Lett. 2016 Oct 28;381(2):380-90. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.011. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27544906
-
Interplay between Trx-1 and S100P promotes colorectal cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition by up-regulating S100A4 through AKT activation.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Apr;22(4):2430-2441. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13541. Epub 2018 Jan 31. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29383839 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and epigenetic down-regulation of microRNA-212 promotes colorectal tumor metastasis via dysregulation of MnSOD.Gastroenterology. 2013 Aug;145(2):426-36.e1-6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23583431
-
The role of the miR-200 family in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer: a systematic review.Int J Cancer. 2018 Jun 15;142(12):2501-2511. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31282. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29388209
-
Oncogenic miRNAs and target therapies in colorectal cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Sep;508:77-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 May 11. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32407782 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical significance of microRNA-125b and its contribution to ovarian carcinogenesis.Bioengineered. 2020 Dec;11(1):939-948. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2020.1814660. Bioengineered. 2020. PMID: 32842846 Free PMC article.
-
In Hepatocellular Carcinoma, miRNA-296-3p Targets MSL2 and Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Invasion.J Oncol. 2021 Dec 2;2021:7430468. doi: 10.1155/2021/7430468. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34899909 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of snail in lung cancer: Protocol for a systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jul;97(28):e11539. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011539. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29995827 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms by Which S100A4 Regulates the Migration and Invasion of PGCCs With Their Daughter Cells in Human Colorectal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 21;10:182. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00182. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32154176 Free PMC article.
-
PYY modulates the tumorigenesis and progression of colorectal cancer unveiled by proteomics.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Dec 15;12(12):5500-5515. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36628274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manfredi S, Lepage C, Hatem C, Coatmeur O, Faivre J, Bouvier A-M. Epidemiology and management of liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2006;244:254–259. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000217629.94941.cf. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

