Catalytic intermolecular hydroaminations of unactivated olefins with secondary alkyl amines
- PMID: 28209894
- PMCID: PMC5426363
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aal3010
Catalytic intermolecular hydroaminations of unactivated olefins with secondary alkyl amines
Abstract
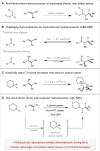
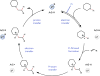
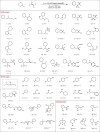
The intermolecular hydroamination of unactivated alkenes with simple dialkyl amines remains an unsolved problem in organic synthesis. We report a catalytic protocol for efficient additions of cyclic and acyclic secondary alkyl amines to a wide range of alkyl olefins with complete anti-Markovnikov regioselectivity. In this process, carbon-nitrogen bond formation proceeds through a key aminium radical cation intermediate that is generated via electron transfer between an excited-state iridium photocatalyst and an amine substrate. These reactions are redox-neutral and completely atom-economical, exhibit broad functional group tolerance, and occur readily at room temperature under visible light irradiation. Certain tertiary amine products generated through this method are formally endergonic relative to their constituent olefin and amine starting materials and thus are not accessible via direct coupling with conventional ground-state catalysts.
Copyright © 2017, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
Comment in
-
Illuminating amination.Science. 2017 Feb 17;355(6326):690-691. doi: 10.1126/science.aam6382. Science. 2017. PMID: 28209858 No abstract available.
References
-
- Coulson DR. Tetrahedron Lett. 1971;12:429–430.
-
- Müller TE, Beller M. Chem Rev. 1998;98:675–704. - PubMed
-
- Huang L, Arndt M, Gooßen K, Heydt H, Gooßen LJ. Chem Rev. 2015;115:2596–2697. - PubMed
-
- Hong S, Marks T. Acc Chem Res. 2004;37:673–686. - PubMed
-
- Utsunomiya M, Kuwano R, Kawatsura M, Hartwig JF. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:5608–5609. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

