Effect of captopril on radiation-induced TGF-β1 secretion in EA.Hy926 human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 28209920
- PMCID: PMC5400550
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15356
Effect of captopril on radiation-induced TGF-β1 secretion in EA.Hy926 human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
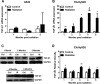
The pathophysiological mechanism involved in the sustained endothelial secretion of cytokines that leads to fibrosis 6-16 months after radiotherapy remains unclear. Angiotensin II (Ang II) is produced by the endothelium in response to stressing stimuli, like radiation, and may induce the synthesis of TGF-β, a profibrotic cytokine. In this study we tested the hypothesis that captopril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, inhibits or attenuates radiation-induced endothelial TGF-β1 secretion. The human endothelial hybrid cell line EA.HY926 was irradiated with split doses of x-rays (28 Gy delivered in 14 fractions of 2 Gy). TGF-β1 mRNA, TNF-α mRNA and TGF-β1 protein levels were evaluated by RT-PCR and western blotting each month until the fifth month post radiation. Ang II was detected using radioimmunoassays, NF-κB activity was examined using EMSA, and western blotting was used to detect the expression of Iκ-Bα. To explore the role of Ang II on radiation-induced TGF-β1 release and Iκ-Bα expression, captopril was added to cultured cells before, during, or after irradiation. Sustained strong expression of TGF-β1 was observed after conventional fractionated irradiation. TNF-α, Ang II, and NF-κB activity were also increased in EA.Hy926 cells after radiation. Captopril decreased Ang II expression, inhibited the NF-κB pathway and reduced TGF-β1 expression. These data suggest that captopril might protect the endothelium from radiation-induced injury.
Keywords: EA.Hy926; NF-κB; TGF-β1; captopril; irradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Brilla CG, Maisch B, Zhou G, Weber KT. Hormonal regulation of cardiac fibroblast function. Eur Heart J. 1995;16:45–50. - PubMed
-
- Pineda JR, Daynac M, Chicheportiche A, Cebrian-Silla A, Sii Felice K, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Boussin FD, Mouthon MA. Vascular-derived TGF-β increases in the stem cell niche and perturbs neurogenesis during aging and following irradiation in the adult mouse brain. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5:548–562. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

