miRNA-21 as a novel therapeutic target in lung cancer
- PMID: 28210157
- PMCID: PMC5310696
- DOI: 10.2147/LCTT.S60341
miRNA-21 as a novel therapeutic target in lung cancer
Abstract
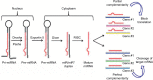
Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer death, and late diagnosis is one of the most important reasons for the high mortality rate. microRNAs (miRNAs) are key players in gene regulation and therefore in tumorigenesis. As far as lung carcinogenesis is concerned, miRNAs open novel fields in biomarker research, in diagnosis, and in therapy. In this review we focus on miR-21 in lung cancer and especially on how miR-21 is involved 1) as a biomarker in response or resistance to therapy or 2) as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: NSCLC; lung cancer; miR-21; response to therapy; therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Spira A, Ettinger DS. Multidisciplinary management of lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:379–392. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–866. - PubMed
-
- Stefani G, Slack FJ. Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:219–230. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

