Genome Insight and Comparative Pathogenomic Analysis of Nesterenkonia jeotgali Strain CD08_7 Isolated from Duodenal Mucosa of Celiac Disease Patient
- PMID: 28210247
- PMCID: PMC5288335
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00129
Genome Insight and Comparative Pathogenomic Analysis of Nesterenkonia jeotgali Strain CD08_7 Isolated from Duodenal Mucosa of Celiac Disease Patient
Abstract
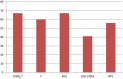
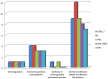
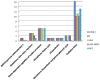
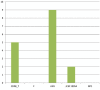
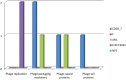
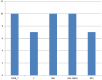
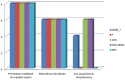
Species of the genus Nesterenkonia have been isolated from different ecological niches, especially from saline habitats and reported as weak human pathogens causing asymptomatic bacteraemia. Here, for the first time we are reporting the genome sequence and pathogenomic analysis of a strain designated as CD08_7 isolated from the duodenal mucosa of a celiac disease patient, identified as Nesterenkonia jeotgali. To date, only five strains of the genus Nesterenkonia (N. massiliensis strain NP1T, Nesterenkonia sp. strain JCM 19054, Nesterenkonia sp. strain F and Nesterenkonia sp. strain AN1) have been whole genome sequenced and annotated. In the present study we have mapped and compared the virulence profile of N. jeotgali strain CD08_7 along with other reference genomes which showed some characteristic features that could contribute to pathogenicity. The RAST (Rapid Annotation using Subsystem Technology) based genome mining revealed more genes responsible for pathogenicity in strain CD08_7 when compared with the other four sequenced strains. The studied categories were resistance to antibiotic and toxic compounds, invasion and intracellular resistance, membrane transport, stress response, osmotic stress, oxidative stress, phages and prophages and iron acquisition. A total of 1431 protein-encoding genes were identified in the genome of strain CD08_7 among which 163 were predicted to contribute for pathogenicity. Out of 163 genes only 59 were common to other genome, which shows the higher levels of genetic richness in strain CD08_7 that may contribute to its functional versatility. This study provides a comprehensive analysis on genome of N. jeotgali strain CD08_7 and possibly indicates its importance as a clinical pathogen.
Keywords: Nesterenkonia jeotgali; RAST; celiac disease; comparative genomics; genome sequencing; gut; pathogenicity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome sequence and description of Nesterenkonia massiliensis sp. nov. strain NP1(T.).Stand Genomic Sci. 2014 Apr 1;9(3):866-82. doi: 10.4056/sigs.5631022. eCollection 2014 Jun 15. Stand Genomic Sci. 2014. PMID: 25197469 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Sequence of Kocuria polaris Strain CD08_4, an Isolate from the Duodenal Mucosa of a Celiac Disease Patient.Genome Announc. 2017 Oct 26;5(43):e01158-17. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01158-17. Genome Announc. 2017. PMID: 29074657 Free PMC article.
-
Nesterenkonia jeotgali sp. nov., isolated from jeotgal, a traditional Korean fermented seafood.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006 Nov;56(Pt 11):2587-2592. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64266-0. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17082396
-
The genome of the Antarctic polyextremophile Nesterenkonia sp. AN1 reveals adaptive strategies for survival under multiple stress conditions.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2016 Apr;92(4):fiw032. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiw032. Epub 2016 Feb 15. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2016. PMID: 26884466
-
Nesterenkonia aurantiaca sp. nov., an alkaliphilic actinobacterium isolated from Antarctica.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2016 Mar;66(3):1554-1560. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.000917. Epub 2016 Jan 26. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26813578
Cited by
-
Sampling a gradient of red snow algae bloom density reveals novel connections between microbial communities and environmental features.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 22;12(1):10536. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13914-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35732638 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of gut microbiota-based therapies in autoimmune and rheumatic diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 80 randomized controlled trials.BMC Med. 2024 Mar 13;22(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03303-4. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 38475833 Free PMC article.
-
The gut microbiome in pancreatogenic diabetes differs from that of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.Sci Rep. 2021 May 26;11(1):10978. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90024-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34040023 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequence and comparative genomic analysis of a clinically important strain CD11-4 of Janibacter melonis isolated from celiac disease patient.Gut Pathog. 2018 Jan 22;10:2. doi: 10.1186/s13099-018-0229-x. eCollection 2018. Gut Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29387173 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analysis of a halophilic bacterium Nesterenkonia sp. CL21 with ability to produce a diverse group of lignocellulolytic enzymes.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2025 Feb;70(1):71-82. doi: 10.1007/s12223-024-01178-9. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2025. PMID: 38842626
References
-
- Avilés-Jiménez F., Guitron A., Segura-Lopez F., Mendez-Tenorio A., Iwai S., Hernandez-Guerrero A., et al. (2016). Microbiota studies in the bile duct strongly suggest a role for Helicobacter pylori in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 22 e11–e22. 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.10.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baron S. (1996). Medical Microbiology 4th Edn. Galveston, TX: University of Texas Medical Branch. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

