The Dutch Technical-Tactical Tennis Test (D4T) for Talent Identification and Development: Psychometric Characteristics
- PMID: 28210345
- PMCID: PMC5304281
- DOI: 10.1515/hukin-2017-0012
The Dutch Technical-Tactical Tennis Test (D4T) for Talent Identification and Development: Psychometric Characteristics
Abstract
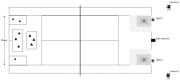
This study examined the test-retest reliability, validity and feasibility of the newly developed Dutch Technical-Tactical Tennis Test (D4T). This new test is relevant for talent identification and development in tennis. Thirty-two youth male tennis players (age 13.4 ± 0.5) were classified as elite (n = 15) or sub-elite (n = 17) according to their position on the national youth ranking list under 15 years (cut-off rank 50) in the Netherlands. Games, rallies and different tactical situations (i.e. offensive, neutral and defensive) were simulated with a ball machine. Players had to return 72 balls to predetermined target areas. Stroke quality was recorded based on ball velocity and accuracy (VA-index), as well as percentage errors. Test-retest reliability was assessed by comparing differences between the first and second test-session (n = 10). An intraclass-correlation coefficient of .78 for the VA-index was found (p < .05), indicating excellent test-retest reliability. Independent t-tests revealed that elite players outscored sub-elite players for the VA-index, ball velocity, accuracy and percentage errors (p < .05), supporting good validity. Furthermore, a high correlation was found between the VA-index and individual positions on the youth ranking list (p = -.75; p < .001). The assessment of feasibility indicated that the D4T was applicable for instructors and coaches. In conclusion, the D4T was shown to be a reliable, valid and feasible test to measure technical-tactical characteristics of tennis performance in youth players.
Keywords: accuracy; ball velocity; field test; performance; racquet sports; youth sports.
Figures



References
-
- Crognier L, Féry YA. Effect of tactical initiative on predicting passing shots in tennis. Appl Cognitive Psych. 2005;19:637–649.
-
- Del Villar F, González LG, Iglesias D, Moreno MP, Cervello EM. Expert-novice differences in cognitive and execution skills during tennis competition 1. Percept Motor Skill. 2007;104:355–365. - PubMed
-
- De Vet HC, Terwee CB, Knol DL, Bouter LM. When to use agreement versus reliability measures. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59:1033–1039. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
