Sildenafil, a Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor, Downregulates Osteopontin in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- PMID: 28210757
- PMCID: PMC5511304
- DOI: 10.1007/s00005-017-0455-9
Sildenafil, a Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor, Downregulates Osteopontin in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Abstract
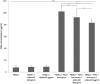
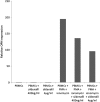
The aim of this study was to investigate the ability of sildenafil to regulate osteopontin (OPN) gene and protein in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy blood donors. OPN is expressed by a wide variety of cell types, including immune cells. OPN functions are linked to various physiological and pathological conditions. Sildenafil is a selective inhibitor of type 5 phosphodiesterase. Sildenafil has recently been found to have immunomodulatory effects in animal models and in studies performed in humans. PMA-stimulated and unstimulated PBMCs from 16 healthy blood donors (men) were cultured with sildenafil (at concentrations of 400 ng/ml and 4 µg/ml). OPN level in culture supernatants was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The analysis of OPN gene expression was performed by real-time PCR. Cell viability was assessed by trypan blue staining. PMA plus ionomycin stimulation of PBMCs resulted in a significant increase of OPN production and gene expression (p < 0.001). Sildenafil significantly decreased OPN secretion (p < 0.05) and gene expression (p < 0.05) in stimulated PBMCs; however, had no effect on OPN in unstimulated PBMCs. Sildenafil did not affect PBMCs viability. Sildenafil downregulates OPN in PBMCs from healthy men. Despite accumulating evidence for the immunomodulatory effects of sildenafil on human immune system cells, further studies are needed to determine if this drug affects the level of cGMP and NF-κB in PBMCs. In addition, it is needed to evaluate sildenafil's activity in PBMCs from patients with elevated OPN levels.
Keywords: Immune response; Osteopontin; PDE5 inhibitor; Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; Sildenafil.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Afify MF, Mohamed GB, El-Maboud MA, et al. Plasma concentration of osteopontin (OPN) in children with systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship with disease activity. Open Autoimmun J. 2009;1:59–63. doi: 10.2174/1876894600901010059. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

