Endothelial glycocalyx as a critical signalling platform integrating the extracellular haemodynamic forces and chemical signalling
- PMID: 28211170
- PMCID: PMC5542909
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13081
Endothelial glycocalyx as a critical signalling platform integrating the extracellular haemodynamic forces and chemical signalling
Abstract
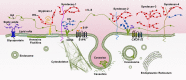
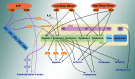
The glycocalyx covers the human mammalian cells and plays important roles in stroke, inflammation and atherosclerosis. It has also been shown to be involved in endothelial mechanotransduction of shear stress. Shear stress induces the remodelling of the major component of the glycocalyx including glypican-1, a cell membrane heparan sulphate proteoglycan. Other factors, such as sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), protect the glycocalyx against syndecan-1 ectodomain shedding and induce the synthesis of heparan sulphate. In this study, we reviewed the role of shear stress and S1P in glycocalyx remodelling and revealed that the glycocalyx is a critical signalling platform, integrating the extracellular haemodynamic forces and chemical signalling, such as S1P, for determining the fate of endothelial cells and vascular diseases. This review integrated our current understanding of the structure and function of the glycocalyx and provided new insight into the role of the glycocalyx that might be helpful for investigating the underlying biological mechanisms in certain human diseases, such as atherosclerosis.
Keywords: glycocalyx; shear stress; sphingosine-1-phosphate.
© 2017 The Author. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate protects endothelial glycocalyx by inhibiting syndecan-1 shedding.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Feb;306(3):H363-72. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00687.2013. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24285115 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Glycocalyx-Mediated Nitric Oxide Production in Response to Selective AFM Pulling.Biophys J. 2017 Jul 11;113(1):101-108. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.05.033. Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 28700908 Free PMC article.
-
Co-therapy with S1P and heparan sulfate derivatives to restore endothelial glycocalyx and combat pro-atherosclerotic endothelial dysfunction.Life Sci. 2025 Sep 15;377:123662. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123662. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40280298
-
Mechanosensing at the vascular interface.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2014 Jul 11;16:505-32. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071813-104908. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2014. PMID: 24905872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Endothelial Surface Glycocalyx in Mechanosensing and Transduction.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1097:1-27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-96445-4_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30315537 Review.
Cited by
-
Atherosclerosis and endothelial mechanotransduction: current knowledge and models for future research.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023 Feb 1;324(2):C488-C504. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00449.2022. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36440856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycocalyx Components Detune the Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanoparticles in a Size- and Charge-Dependent Manner.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023 Jan 16;6(1):64-73. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.2c00595. Epub 2022 Oct 14. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023. PMID: 36239448 Free PMC article.
-
Human collecting lymphatic glycocalyx identification by electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 21;13(1):3022. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30043-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36810649 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Biohybrid Lung Development-Fibronectin-Coating Bestows Hemocompatibility of Gas Exchange Hollow Fiber Membranes by Improving Flow-Resistant Endothelialization.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Dec 27;12(1):35. doi: 10.3390/membranes12010035. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35054561 Free PMC article.
-
Glycocalyx Impairment in Vascular Disease: Focus on Inflammation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 13;9:730621. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.730621. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34589494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tarbell JM, Ebong EE: The endothelial glycocalyx: a mechano‐sensor and ‐transducer. Science signaling 1: pt8, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Becker BF, Chappell D, Bruegger D, et al Therapeutic strategies targeting the endothelial glycocalyx: acute deficits, but great potential. Cardiovasc Res. 2010; 87: 300–10. - PubMed
-
- Haeren RH, van de Ven SE, van Zandvoort MA, et al Assessment and imaging of the cerebrovascular glycocalyx. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2016; 13: 249–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

