Soil wettability can be explained by the chemical composition of particle interfaces - An XPS study
- PMID: 28211469
- PMCID: PMC5314406
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42877
Soil wettability can be explained by the chemical composition of particle interfaces - An XPS study
Abstract
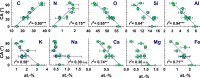
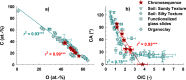
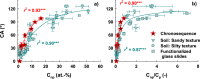
Soil wettability (quantified in terms of contact angle, CA) is crucial for physical, chemical, and biological soil functioning. As the CA is determined by components present within the outmost nanometer of particles, this study applied X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) with a maximum analysis depth of 10 nm to test the relationship between CA and surface elemental composition, using soil samples from a chronosequence where CA increased from 0° (0 yrs) to about 98° (120 yrs). Concurrently, as seen by XPS, C and N content increased and the content of O and the mineral-derived cations (Si, Al, K, Na, Ca, Mg, Fe) decreased. The C content was positively correlated with CA and least squares fitting indicated increasing amounts of non-polar C species with soil age. The contents of O and the mineral-derived cations were negatively correlated with CA, suggesting an increasing organic coating of the minerals that progressively masked the underlying mineral phase. The atomic O/C ratio was found to show a close negative relationship with CA, which applied as well to further sample sets of different texture and origin. This suggests the surface O/C ratio to be a general parameter linking surface wettability and surface elemental composition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bachmann J., Deurer M. & Arye G. Modeling water movement in heterogeneous water-repellent soil: 1. Development of a contact angle–dependent water-retention model. Vadose Zone J. 6, 436–445 (2007).
-
- Young T. An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 95, 65–87 (1805).
-
- Doerr S. H., Shakesby R. A. & Walsh R. P. D. Soil water repellency: its causes, characteristics and hydro-geomorphological significance. Earth Sci. Rev. 51, 33–65 (2000).
-
- Ma’shum M.; Tate M. E.; Jones G. P. & Oades J. M. Extraction and characterization of water-repellent materials from Australian soils. J. Soil Sci. 39, 99–110 (1988).
-
- Chorover J., Kretzschmar R., Garcia-Pichel F. & Sparks D. L. Soil biogeochemical processes within the critical zone. Elements 3, 321–326 (2007).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

