Inhibition of PDE5A1 guanosine cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) hydrolysing activity by sildenafil analogues that inhibit cellular cGMP efflux
- PMID: 28211580
- PMCID: PMC5434896
- DOI: 10.1111/jphp.12693
Inhibition of PDE5A1 guanosine cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) hydrolysing activity by sildenafil analogues that inhibit cellular cGMP efflux
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the ability of 11 sildenafil analogues to discriminate between cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (cnPDEs) and to characterise their inhibitory potencies (Ki values) of PDE5A1-dependent guanosine cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) hydrolysis.
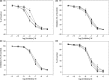
Methods: Sildenafil analogues were identified by virtual ligand screening (VLS) and screened for their ability to inhibit adenosine cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) hydrolysis by PDE1A1, PDE1B1, PDE2A1, PDE3A, PDE10A1 and PDE10A2, and cGMP hydrolysis by PDE5A, PDE6C, PDE9A2 for a low (1 nm) and high concentration (10 μm). Complete IC50 plots for all analogues were performed for PDE5A-dependent cGMP hydrolysis. Docking studies and scoring were made using the ICM molecular modelling software.
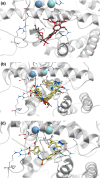
Key findings: The analogues in a low concentration showed no or low inhibition of PDE1A1, PDE1B1, PDE2A1, PDE3A, PDE10A1 and PDE10A2. In contrast, PDE5A and PDE6C were markedly inhibited to a similar extent by the analogues in a low concentration, whereas PDE9A2 was much less inhibited. The analogues showed a relative narrow range of Ki values for PDE5A inhibition (1.2-14 nm). The sildenafil molecule was docked in the structure of PDE5A1 co-crystallised with sildenafil. All the analogues had similar binding poses as sildenafil.
Conclusions: Sildenafil analogues that inhibit cellular cGMP efflux are potent inhibitors of PDE5A and PDE6C.
Keywords: PDE5; guanosine cyclic monophosphate; inhibitors; molecular modelling; sildenafil analogues.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Royal Pharmaceutical Society.
Figures
References
-
- Conti M, Beavo J. Biochemistry and physiology of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: essential components in cyclic nucleotide signaling. Annu Rev Biochem 2007; 76: 481–511. - PubMed
-
- Jedlitschky G et al The multidrug resistance protein 5 functions as an ATP‐dependent export pump for cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 30069–30074. - PubMed
-
- Corbin JD et al Phosphodiesterase type 5 as a pharmacologic target in erectile dysfunction. Urology 2002; 60: 4–11. - PubMed
-
- Sundkvist E et al Pharmacological characterization of the ATP‐dependent low K(m) guanosine 3′,5′‐cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) transporter in human erythrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 2002; 63: 945–949. - PubMed

