Data quality assurance and control in cognitive research: Lessons learned from the PREDICT-HD study
- PMID: 28211597
- PMCID: PMC6258197
- DOI: 10.1002/mpr.1534
Data quality assurance and control in cognitive research: Lessons learned from the PREDICT-HD study
Abstract
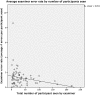
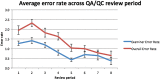
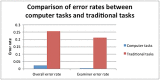
We discuss the strategies employed in data quality control and quality assurance for the cognitive core of Neurobiological Predictors of Huntington's Disease (PREDICT-HD), a long-term observational study of over 1,000 participants with prodromal Huntington disease. In particular, we provide details regarding the training and continual evaluation of cognitive examiners, methods for error corrections, and strategies to minimize errors in the data. We present five important lessons learned to help other researchers avoid certain assumptions that could potentially lead to inaccuracies in their cognitive data.
Keywords: cognitive assessment; quality assurance; quality control.
Copyright © 2017 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Anastasi, A. (1988). Psychological testing. New York: Macmillan.
-
- Benedict, R. H. B. , Schretlen, D. , Groninger, L. , & Brandt, J. (1998). Hopkins Verbal Learning Test Revised: Normative data and analysis of inter‐form and test–retest reliability. Clinical Neuropsychologist, 12(1), 43–55. doi: 10.1076/clin.12.1.43.1726 - DOI
-
- McCaffrey R. J., Duff K., & Westervelt H. J. (Eds) (2000). Practitioner's Guide to Evaluating Change with Neuropsychological Assessment Instruments. New York: Academic/Plenum Publishers;
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical