Mice and the A-Bomb: Irradiation Systems for Realistic Exposure Scenarios
- PMID: 28211757
- PMCID: PMC5525049
- DOI: 10.1667/RR008CC.1
Mice and the A-Bomb: Irradiation Systems for Realistic Exposure Scenarios
Abstract
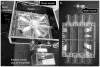
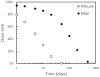
Validation of biodosimetry assays is normally performed with acute exposures to uniform external photon fields. Realistically, exposure to a radiological dispersal device or reactor leak will include exposure to low dose rates and likely exposure to ingested radionuclides. An improvised nuclear device will likely include a significant neutron component in addition to a mixture of high- and low-dose-rate photons and ingested radionuclides. We present here several novel irradiation systems developed at the Center for High Throughput Minimally Invasive Radiation Biodosimetry to provide more realistic exposures for testing of novel biodosimetric assays. These irradiators provide a wide range of dose rates (from Gy/s to Gy/week) as well as mixed neutron/photon fields mimicking an improvised nuclear device.
Figures




References
-
- Grace MB, Moyer BR, Prasher J, Cliffer KD, Ramakrishnan N, Kaminski J, et al. Rapid Radiation Dose Assessment for Radiological Public Health Emergencies: Role of NIAID and BARDA. Health Phys. 2010;98(2):172–78. - PubMed
-
- Biological and Environmental Effects of Nuclear War, Summary-Analysis of Hearings. Joint Committee on Atomic Energy. Place Government Printing Office: Government Printing Office; 1959.
-
- Survival of the Relocated Population of the U.S. after a Nuclear Attack. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory; 1976. Report No. ORNL-5041. ( http://oai.dtic.mil/oai/oai?verb=getRecord&metadataPrefix=html&identifie...)
-
- Subcommittee on Health and Scientific Research of the Committee on Labor and Human Resources, United States Senate Place U.S. Government Printing Office. U.S. Government Printing Office; 1980. Short- and Long-Term Health Effects of the Surviving Population of a Nuclear War.
-
- Sidel VW, Geiger HJ, Lown B. The physician’s role in the postattack period. New Eng J Med. 1962;266(22):1137–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

