99mTc-MAG3: Image Wisely
- PMID: 28212051
- PMCID: PMC5495132
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2017152311
99mTc-MAG3: Image Wisely
Abstract
Purpose To determine if commonly administered doses of technetium 99m (99mTc) mertiatide (MAG3) in the range of 300-370 MBq (approximately 8-10 mCi) contribute to image interpretation and justify the resulting radiation exposure. Materials and Methods The respective institutional review boards approved this HIPAA-compliant study and waived informed consent. Baseline and furosemide 99mTc-MAG3 imaging examinations in 50 patients suspected of having renal obstruction and 48 patients suspected of having renovascular hypertension (RVH) were randomly selected from archived databases and were independently scored by three experienced readers without access to 2-second flow images. Readers were blinded to their original scores, and then they rescored each examination with access to high-activity 2-second flow images. Relative renal function was determined after a low activity (62.9 MBq ± 40.7) baseline acquisition for RVH and a high activity (303.4 MBq ± 48.1) acquisition after administration of enalaprilat. Data were analyzed by using random effects analysis of variance and mean and standard error of the mean for the difference between sets of scores and the difference between relative function measurements. Results There was no significant difference in the scores without flow images compared with blinded scores with high-activity flow images for patients suspected of having obstruction (P = .80) or RVH (P = .24). Moreover, there was no significant difference in the relative uptake measurements after administration of low and high activities (P > .99). Conclusion Administered doses of 99mTc-MAG3 in the range of 300-370 MBq (approximately 8-10 mCi) do not affect the relative function measurements or contribute to interpretation of images in patients suspected of having RVH or obstruction compared with administration of lower doses; unnecessary radiation exposure can be avoided by administering doses in the range of 37-185 MBq as recommended incurrent guidelines. © RSNA, 2017.
Figures


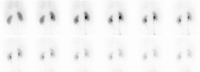




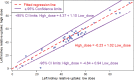
References
-
- O’Reilly P, Aurell M, Britton K, Kletter K, Rosenthal L, Testa T. Consensus on diuresis renography for investigating the dilated upper urinary tract. Radionuclides in Nephrourology Group. Consensus Committee on Diuresis Renography. J Nucl Med 1996;37(11):1872–1876. - PubMed
-
- Shulkin BL, Mandell GA, Cooper JA, et al. . Procedure guideline for diuretic renography in children 3.0. J Nucl Med Technol 2008;36(3):162–168. - PubMed
-
- Gordon I, Piepsz A, Sixt R; Auspices of Paediatric Committee of European Association of Nuclear Medicine . Guidelines for standard and diuretic renogram in children. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2011;38(6):1175–1188. - PubMed
-
- Mallinckrodt Website . Technescan MAG3 Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mertiatide. http://www.mallinckrodt.com/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=616. Accessed July 2, 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

