Feasibility of an implementation strategy for the integration of health promotion in routine primary care: a quantitative process evaluation
- PMID: 28212621
- PMCID: PMC5316192
- DOI: 10.1186/s12875-017-0585-5
Feasibility of an implementation strategy for the integration of health promotion in routine primary care: a quantitative process evaluation
Abstract
Background: Process evaluation is recommended to improve the understanding of underlying mechanisms related to clinicians, patients, context and intervention delivery that may impact on trial or program results, feasibility and transferability to practice. The aim of this study was to assess the feasibility of the Prescribe Healthy Life (PVS from the Spanish "Prescribe Vida Saludable") implementation strategy for enhancing the adoption and implementation of an evidence-based health promotion intervention in primary health care.
Methods: A descriptive study of 2-year implementation indicators for the PVS clinical intervention was conducted in four primary health care centers. A multifaceted collaborative modeling implementation strategy was developed to enhance the integration of a clinical intervention to promote healthy lifestyles into clinical practice. Process indicators were assessed for intervention reach, adoption, implementation, sustainability and their variability at center, practice, and patient levels.
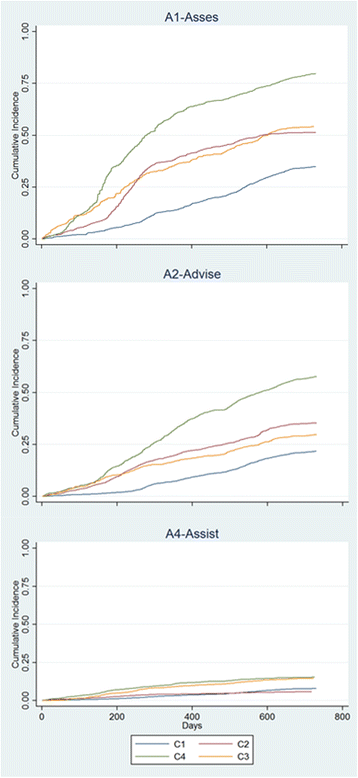
Results: Mean rates of adoption by means of active collaboration among the three main professional categories (family physicians, nurses and administrative personnel) were 75% in all centers. Just over half of the patients that attended (n = 11650; 51.9%) were reached in terms of having their lifestyle habits assessed, while more than a third (33.7%; n = 7433) and almost 10% (n = 2175) received advice or a printed prescription for at least one lifestyle change, respectively. Only 3.7% of the target population received a repeat prescription. These process indicators significantly (p < 0.001) varied by center, lifestyle habit and patient characteristics. Sustainability of intervention components changed thorough the implementation period within centers.
Conclusions: The implementation strategy used showed moderate-to-good performance on process indicators related to adoption, reach, and implementation of the evidence-based healthy lifestyle promotion intervention in the context of routine primary care. Sources of heterogeneity and instability in these indicators may improve our understanding of factors required to attain adequate program adoption and implementation through improved implementation strategies.
Keywords: Health promotion; Implementation; Primary Health Care; Process evaluation.
Figures
References
-
- Medical Research Council . Developing and evaluating complex interventions: new guidance. London: Medical Research Council; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials