Lipid peroxidation in cell death
- PMID: 28212725
- PMCID: PMC5319403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.086
Lipid peroxidation in cell death
Abstract
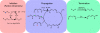
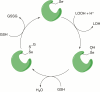
Disruption of redox homeostasis is a key phenotype of many pathological conditions. Though multiple oxidizing compounds such as hydrogen peroxide are widely recognized as mediators and inducers of oxidative stress, increasingly, attention is focused on the role of lipid hydroperoxides as critical mediators of death and disease. As the main component of cellular membranes, lipids have an indispensible role in maintaining the structural integrity of cells. Excessive oxidation of lipids alters the physical properties of cellular membranes and can cause covalent modification of proteins and nucleic acids. This review discusses the synthesis, toxicity, degradation, and detection of lipid peroxides in biological systems. Additionally, the role of lipid peroxidation is highlighted in cell death and disease, and strategies to control the accumulation of lipid peroxides are discussed.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Ferroptosis; Lipid oxidation; Neurodegeneration; Oxidation; Peroxidation.
Copyright © 2016 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Turini ME, DuBois RN. Cyclooxygenase-2: a therapeutic target. Annu Rev Med. 2002;53:35–57. - PubMed
-
- Breuer W, Shvartsman M, Cabantchik ZI. Intracellular labile iron. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40:350–354. - PubMed
-
- Marisa Repetto JS, Boveris Alberto. Lipid peroxidation: chemical mechanism, biological implications and analytical determination. In: Catala DA, editor. Lipid Peroxiation. InTech; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

