Inhibition of Inflammatory Gene Transcription by IL-10 Is Associated with Rapid Suppression of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Enhancer Activation
- PMID: 28213503
- PMCID: PMC5369026
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601781
Inhibition of Inflammatory Gene Transcription by IL-10 Is Associated with Rapid Suppression of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Enhancer Activation
Abstract
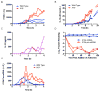
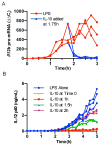
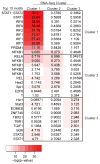
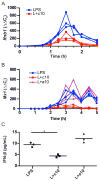
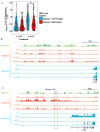
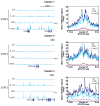
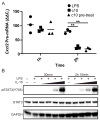
IL-10 limits the magnitude of inflammatory gene expression following microbial stimuli and is essential to prevent inflammatory disease; however, the molecular basis for IL-10-mediated inhibition remains elusive. Using a genome-wide approach, we demonstrate that inhibition of transcription is the primary mechanism for IL-10-mediated suppression in LPS-stimulated macrophages and that inhibited genes can be divided into two clusters. Genes in the first cluster are inhibited only if IL-10 is included early in the course of LPS stimulation and is strongly enriched for IFN-inducible genes. Genes in the second cluster can be rapidly suppressed by IL-10 even after transcription is initiated, and this is associated with suppression of LPS-induced enhancer activation. Interestingly, the ability of IL-10 to rapidly suppress active transcription exhibits a delay following LPS stimulation. Thus, a key pathway for IL-10-mediated suppression involves rapid inhibition of enhancer function during the secondary phase of the response to LPS.
Copyright © 2017 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Amit I, Garber M, Chevrier N, Leite AP, Donner Y, Eisenhaure T, Guttman M, Grenier JK, Li W, Zuk O, Schubert LA, Birditt B, Shay T, Goren A, Zhang X, Smith Z, Deering R, McDonald RC, Cabili M, Bernstein BE, Rinn JL, Meissner A, Root DE, Hacohen N, Regev A. Unbiased Reconstruction of a Mammalian Transcriptional Network Mediating Pathogen Responses. Science. 2009;326:257–263. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doyle SE, Vaidya SA, O’Connell R, Dadgostar H, Dempsey PW, Wu TT, Rao G, Sun R, Haberland ME, Modlin RL, Cheng G. IRF3 Mediates a TLR3/TLR4-Specific Antiviral Gene Program. Immunity. 2002;17:251–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

