Somatic Mutations in TSC1 and TSC2 Cause Focal Cortical Dysplasia
- PMID: 28215400
- PMCID: PMC5339289
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.01.030
Somatic Mutations in TSC1 and TSC2 Cause Focal Cortical Dysplasia
Abstract
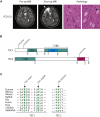
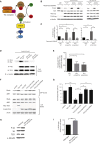
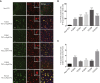
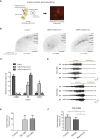
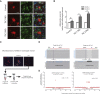
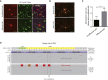
Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) is a major cause of the sporadic form of intractable focal epilepsies that require surgical treatment. It has recently been reported that brain somatic mutations in MTOR account for 15%-25% of FCD type II (FCDII), characterized by cortical dyslamination and dysmorphic neurons. However, the genetic etiologies of FCDII-affected individuals who lack the MTOR mutation remain unclear. Here, we performed deep hybrid capture and amplicon sequencing (read depth of 100×-20,012×) of five important mTOR pathway genes-PIK3CA, PIK3R2, AKT3, TSC1, and TSC2-by using paired brain and saliva samples from 40 FCDII individuals negative for MTOR mutations. We found that 5 of 40 individuals (12.5%) had brain somatic mutations in TSC1 (c.64C>T [p.Arg22Trp] and c.610C>T [p.Arg204Cys]) and TSC2 (c.4639G>A [p.Val1547Ile]), and these results were reproducible on two different sequencing platforms. All identified mutations induced hyperactivation of the mTOR pathway by disrupting the formation or function of the TSC1-TSC2 complex. Furthermore, in utero CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing of Tsc1 or Tsc2 induced the development of spontaneous behavioral seizures, as well as cytomegalic neurons and cortical dyslamination. These results show that brain somatic mutations in TSC1 and TSC2 cause FCD and that in utero application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system is useful for generating neurodevelopmental disease models of somatic mutations in the brain.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing; TSC1; TSC2; brain mosaicism; brain somatic mutation; focal cortical dysplasia; intractable epilepsy.
Copyright © 2017 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Blümcke I., Vinters H.V., Armstrong D., Aronica E., Thom M., Spreafico R. Malformations of cortical development and epilepsies: neuropathological findings with emphasis on focal cortical dysplasia. Epileptic Disord. 2009;11:181–193. - PubMed
-
- Sisodiya S.M. Surgery for malformations of cortical development causing epilepsy. Brain. 2000;123:1075–1091. - PubMed
-
- Bast T., Ramantani G., Seitz A., Rating D. Focal cortical dysplasia: prevalence, clinical presentation and epilepsy in children and adults. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2006;113:72–81. - PubMed
-
- Tassi L., Colombo N., Garbelli R., Francione S., Lo Russo G., Mai R., Cardinale F., Cossu M., Ferrario A., Galli C. Focal cortical dysplasia: neuropathological subtypes, EEG, neuroimaging and surgical outcome. Brain. 2002;125:1719–1732. - PubMed
-
- Fauser S., Huppertz H.J., Bast T., Strobl K., Pantazis G., Altenmueller D.M., Feil B., Rona S., Kurth C., Rating D. Clinical characteristics in focal cortical dysplasia: a retrospective evaluation in a series of 120 patients. Brain. 2006;129:1907–1916. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

