Radiolabeling and initial biological evaluation of [18F]KBM-1 for imaging RAR-α receptors in neuroblastoma
- PMID: 28216044
- PMCID: PMC5724519
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.01.093
Radiolabeling and initial biological evaluation of [18F]KBM-1 for imaging RAR-α receptors in neuroblastoma
Abstract
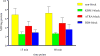
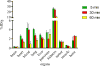
Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR-α) plays a significant role in a number of diseases, including neuroblastoma. Children diagnosed with high-risk neuroblastoma are treated13-cis-retinoic acid, which reduces risk of cancer recurrence. Neuroblastoma cell death is mediated via RAR-α, and expression of RAR-α is upregulated after treatment. A molecular imaging probe that binds RAR-α will help clinicians to diagnose and stratify risk for patients with neuroblastoma, who could benefit from retinoid-based therapy. In this study, we report the radiolabeling, and initial in vivo evaluation of [18F]KBM-1, a novel RAR-α agonist. The radiochemical synthesis of [18F]KBM-1 was carried out through KHF2 assisted substitution of [18F]- from aryl-substituted pinacolatoesters-based retinoid precursor. In vitro cell uptake assay in human neuroblastoma cell line showed that the uptake of [18F]KBM-1 was significantly inhibited by all three blocking agents (KBM-1, ATRA, BD4) at all the selected incubation times. Standard biodistribution in mice bearing neuroblastoma tumors demonstrated increased tumor uptake from 5min to 60min post radiotracer injection and the uptake ratios for target to non-target (tumor: muscle) increased 2.2-fold to 3.7-fold from 30min to 60min post injection. Tumor uptake in subset of 30min blocking group was 1.7-fold lower than unblocked. These results demonstrate the potential utility of [18F]KBM-1 as a RAR-α imaging agent.
Keywords: All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA); Biodistribution; Neuroblastoma; Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR-α).
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Boylan JF, Lufkin T, Achkar CC, Taneja R, Chambon P, Gudas LJ. Targeted disruption of retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR alpha) and RAR gamma results in receptor-specific alterations in retinoic acid-mediated differentiation and retinoic acid metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:843–851. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Niederreither K, Dolle P. Retinoic acid in development: towards an integrated view. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:541–553. - PubMed
-
- Chambon P. A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 1996;10:940–954. - PubMed
-
- Chambon P. The retinoid signaling pathway: molecular and genetic analyses. Semin Cell Biol. 1994;5:115–125. - PubMed
-
- Dimberg A. The Role of Stat1 in Retinoic Acid-induced Myelomonocytic Differentiation of Human Leukemia Cells. 2002
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

